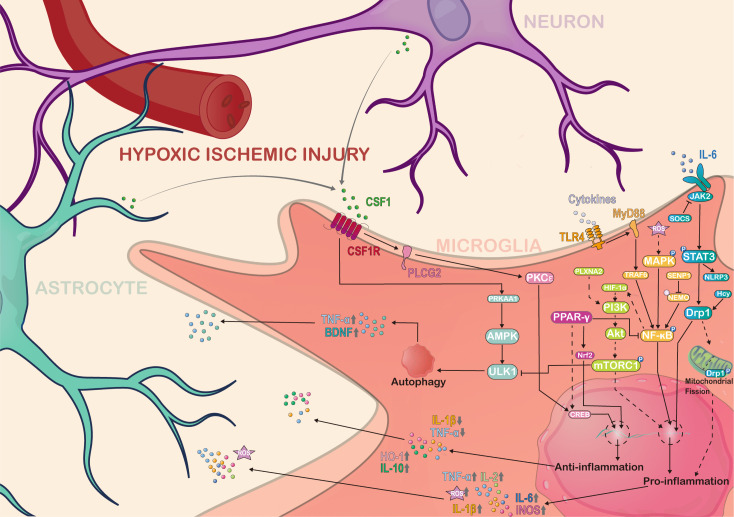
Figure 1.
Molecular complexity and regulatory pathways of microglia in hypoxia ischemic brain injury. Microglia are complex regulated by various pathways in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury, and also interact with other cells and molecules in the central nervous system to secrete various cytokines, chemokines and neuroregulatory molecules to regulate the homeostasis of the CNS niche. Solid-lined arrows represent the mechanisms previously examined in the literature. Dotted arrows indicate potential mediating pathways that have not been fully investigated from previous work. AMPK, Adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase; Akt, known as protein kinase B; PRKAA1, Protein Kinase AMP-Activated Catalytic Subunit Alpha 1; PKCϵ, Protein kinases C ϵ isoforms; ULK1, Unc-51 Like Autophagy Activating Kinase 1; MAPK, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase; CSF1, Colony Stimulating Factor 1; CSF1R, Colony Stimulating Factor 1 Receptor; PLCG2, Phospholipase C Gamma 2; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa-B; S, Small ubiquitin-like modifier; SENP1, SUMO Specific Peptidase 1; NEMO, NF-kappa-B essential modulator; PPAR-γ, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; CREB, Cyclic AMP response element binding protein; Nrf2, Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Hif-1α, Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha; TRAF6, Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; MyD88, Myeloid differentiation primary response 88; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; PI3K, Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; SOCS, Suppressor of cytokine signaling; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; STAT3, Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; Drp1, Dynamin-related protein 1; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor alpha; BDNF, Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; IL, Interleukin; iNOS, Inducible nitric oxide synthase; HO-1, Heme oxygenase 1. This figure was created by Adobe Illustrator software.