Fig. (1).
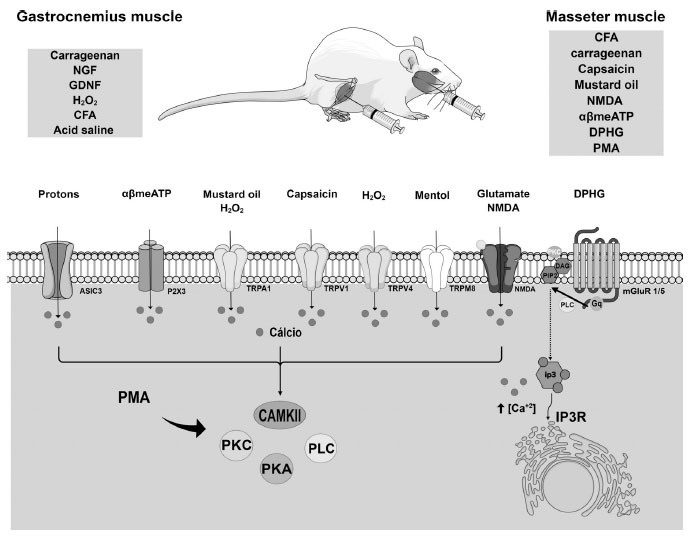
Models of muscular hyperalgesia in the gastrocnemius and masseter muscle in rodents and the participation of transient receptor potential receptors (TRPs). The different models of muscle hyperalgesia in the masseter muscle used algogenic substances, such as complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA), carrageenan, capsaicin (TRPV1 agonist), mustard oil (TRPA1 agonist), N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA, TRPA1 activator), alphabetameATP (αβmeATP, TRPA1 activator), dihydroxyphenylglycine (DPHG, mGlu1/5 agonist), phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, an activator of PKC), capsaicin (TRPV1 agonist), or mustard oil (TRPA1 and TRPV4 agonist). The models of muscle hyperalgesia in the gastrocnemius muscle used nociceptive substances such as CFA, carrageenan, nerve growth factor (NGF promotes proliferation, degranulation, and release of inflammatory mediators from immune cells), glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF promotes proliferation, degranulation, and release of inflammatory mediators from immune cells), H2O2 (TRPA1 and TRPV4 agonist), and acid saline (promotes acidosis that activates TRPs and ASIC3), ATP (activates P2X3). The indirect or direct release of calcium by activating these receptors leads to the activation of protein kinases such as PKA, PKC, PLC, and CAMKII. In this sense, these mechanisms have the capability to trigger multiple pain and inflammation signaling pathways.
