Fig. 3.
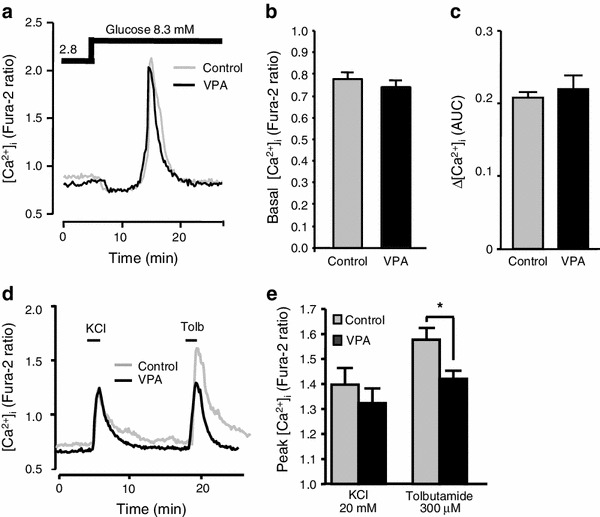
Effects of long-term exposure to VPA on subsequent [Ca2+]i responses in β-cells. a Elevation of glucose concentration from 2.8 mM to 8.3 mM increased [Ca2+]i in control and long-term VPA (200 μg/ml)-treated β-cells in a similar manner. The results are representative of 35 control and 43 VPA-treated cells. b [Ca2+]i levels in the presence of a basal 2.8 mM glucose in β-cells after control culture (gray bar) and after culture with VPA (black bar). c Average area under curve (AUC) of [Ca2+]i increases in response to 8.3 mM glucose for 10 min in β-cells after control culture (gray bar) and after culture with VPA (black bar). d 20 mM KCl and 300 μM tolbutamide (Tolb), a KATP channel blocker, increased [Ca2+]i in β-cells after control culture and after culture with VPA (200 μg/ml). VPA selectively attenuated [Ca2+]i response to Tolb. The result is representative of 35 β-cells. e Average peaks of [Ca2+]i responses to KCl and Tolb in β-cells after control culture (gray bar) and after culture with VPA (black bar). Average peak [Ca2+]i response to Tolb was significantly reduced in β-cells exposed to VPA. n = 4. *p < 0.01
