Fig. 2.
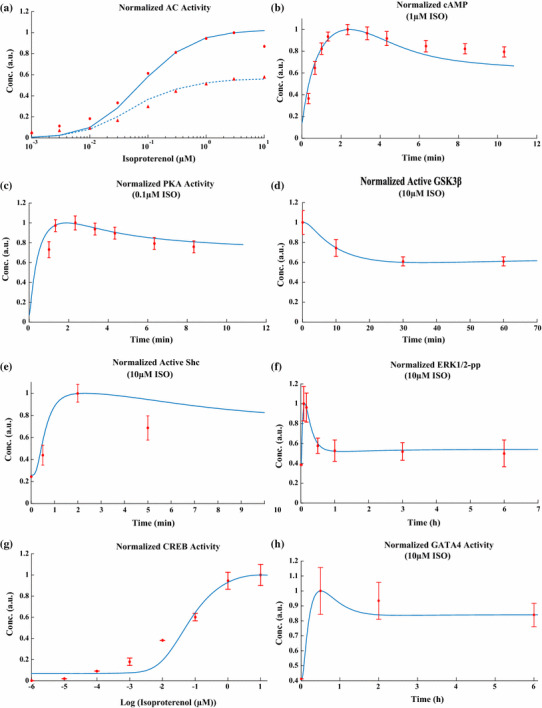
Estimation of kinetic parameters for β-adrenergic classical and non-classical signaling pathways. a The sensitivity of normalized AC activity over basal to isoproterenol for maximal AC activity (simulation solid line and experimental filled circle) and AC activity after 30 min of ISO stimulation (simulation dashed line and experimental filled triangle). The experimental data were obtained from Freedman et al.’s study [21] for β1-AR stimulation and its desensitization through GRK2 mechanism. b The time course of normalized cAMP level after indicated ISO stimulation. The experimental data were obtained from De Arcangelis et al.’s study [18]. c The time course of normalized PKA activity after indicated ISO stimulation. The experimental data were obtained from De Arcangelis et al.’s study [18]. d The time course of normalized active GSK3β after indicated ISO stimulation. The experimental data were obtained from Morisco et al.’s study [41]. e The time course of normalized active Shc after indicated ISO stimulation. The experimental data were obtained from Zou et al.’s study [69]. f The time course of normalized ERK1/2 pp concentration after indicated ISO stimulation. The experimental data were obtained from Shin et al.’s study [56]. g The sensitivity of normalized steady-state activity of CREB to isoproterenol. The experimental data were obtained from Yang et al.’s study [66]. h The time course of normalized GATA4 activity after indicated ISO stimulation. The experimental data were obtained from Morisco et al.’s study [42]. For b–h, simulation results are indicated by solid lines and experimental data are indicated by filled circles. The experimental data are mean ± SE of at least three independent experiments
