Fig. 4.
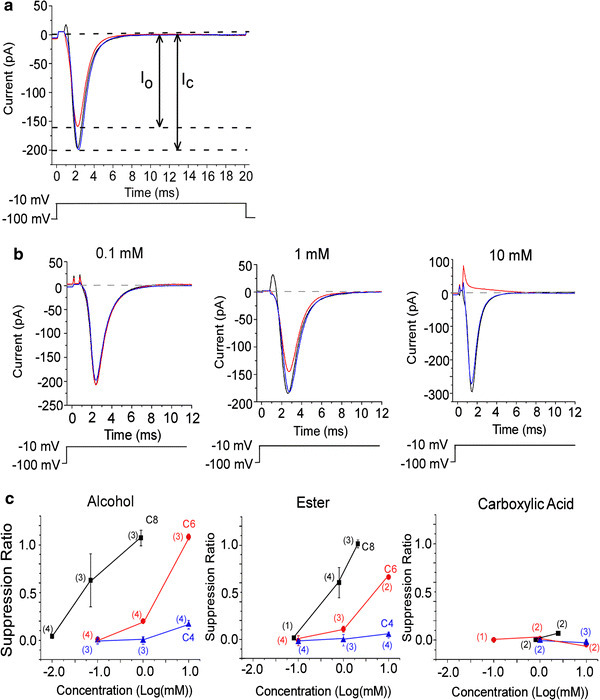
Suppression of voltage-gated Na current by odorants. The voltage-gated Na current was evoked by a depolarization pulse to −10 mV (20 ms) from V
h of −100 mV. The leak current obtained in choline solution was subtracted. a, b
Black traces show currents in control solution, red trace currents in odorant solution, blue trace current recovery. a Reduction of voltage-gated Na current by C6 alcohol (1 mM). Upward deflection of bottom trace indicates the timing and duration of the voltage pulse. The suppression ratio is 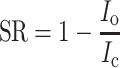 (I
c: I
Na peak in the control solution, I
o: peak current in the odorant solution). These data show SR = 0.19. b Suppression of voltage-gated Na current by 3 different concentrations of C6 alcohol. Average of 30 recordings. Upward deflection of bottom trace indicates the timing and duration of the voltage pulse. Suppression ratios were −0.51 × 10−2 (0.1 mM), 0.22 (1 mM), and 1.06 (10 mM). c Correlation between odorant concentration and suppression ratio. Black squares show C8 chemicals (alcohols, esters, and carboxylic acids), red circles are C6, and blue triangles are C4. Error bars show SD. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of trial cells
(I
c: I
Na peak in the control solution, I
o: peak current in the odorant solution). These data show SR = 0.19. b Suppression of voltage-gated Na current by 3 different concentrations of C6 alcohol. Average of 30 recordings. Upward deflection of bottom trace indicates the timing and duration of the voltage pulse. Suppression ratios were −0.51 × 10−2 (0.1 mM), 0.22 (1 mM), and 1.06 (10 mM). c Correlation between odorant concentration and suppression ratio. Black squares show C8 chemicals (alcohols, esters, and carboxylic acids), red circles are C6, and blue triangles are C4. Error bars show SD. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of trial cells
