Fig. 6.
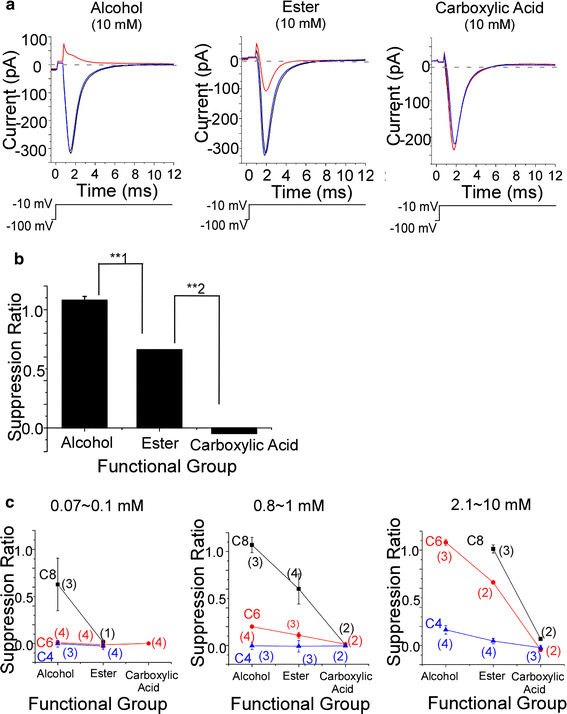
Dependence of suppression ratio on functional group. Alcohols, esters, and carboxylic acids were used as odorants in extracellular perfusion solutions. Current was evoked by depolarization to −10 mV (20 ms) from V h of −100 mV. The leak current obtained in choline solution was subtracted from all current waveforms. a Current waveform in solutions of the C6 chemicals. Average of 30 recordings. Upward deflection of bottom trace indicates the timing and duration of the voltage pulse. Black trace control, red trace odorant, blue trace recovery. The suppression ratio for the alcohol (10 mM) was 1.11. That for the ester (10 mM) was 0.66. That for the carboxylic acid (10 mM) was −0.50 × 10−2. b Suppression ratio for each functional group. Suppression ratio for C6 alcohol (10 mM) was 1.08 ± 0.31 × 10−1 (n = 3), that for C6 ester (10 mM) was 0.66 (n = 2), that for C6 carboxylic acid (10 mM) was −0.46 × 10−1 (n = 2). Using t test for **1 and **2, p < 0.005. c Relationship between suppression ratio and carbon chain length. Left: black squares were C8 alcohol (0.07 mM) and C8 ester (0.08 mM). Red circles were C6 alcohol (0.1 mM), C6 ester (0.1 mM), and C6 carboxylic acid (0.1 mM). Blue triangles were C4 alcohol (0.1 mM) and C4 ester (0.1 mM). Center: black squares were C8 alcohol (0.9 mM), C8 ester (0.8 mM), and C8 carboxylic acid (0.8 mM). Red circles were C6 alcohol (1 mM), C6 ester (1 mM), and C6 carboxylic acid (1 mM). Blue triangles were C4 alcohol (1 mM), C4 ester (1 mM), and C4 carboxylic acid (1 mM). Right: black squares were C8 ester (2.1 mM) and C8 carboxylic acid (2.5 mM). Red circles were C6 alcohol (10 mM), C6 ester (10 mM), and C6 carboxylic acid (10 mM). Blue triangles were C4 alcohol (10 mM), C4 ester (10 mM), and C4 carboxylic acid (10 mM). Error bars show SD. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of trial cells. Data shown in c were obtained from Fig. 5c
