Fig. 2.
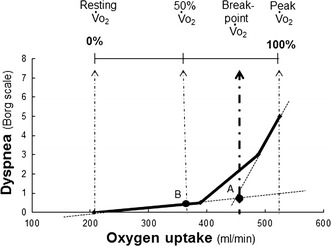
Dyspnea break-point (point A). First, a dyspnea break-point was determined for each patient by using the intersection of two lines on plots of dyspnea as a function of . Second, the location (%) of each resulting dyspnea break-point relative to Δ (= peak − resting ) that occurs during exercise was calculated for each patient by use of the equation 100 × (dyspnea break-point − resting )/Δ. 50 % point (point B). The value at the 50 % point was calculated for each patient by use of the equation resting + (peak − resting )/2. Next, the value of the Borg scale at the 50 % point was calculated for each patient, where the Borg scale on the Y axis corresponded to the 50 % point on the X axis by linear interpolation between adjacent measurement points
