Fig. 2.
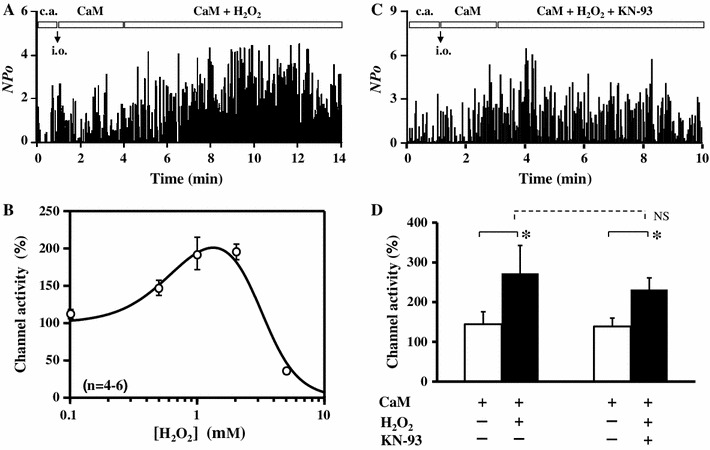
H2O2-mediated facilitation of Ca2+ channel activity in inside-out mode. a, c Time course of channel activity (NPo) recorded in the cell-attached (c.a.) mode followed by the inside-out (i.o.) mode, in which channel activity was maintained with 1 μM CaM + 3 mM ATP, and then 1 mM H2O2 without (a) or with (c); 10 μM KN-93 was additionally applied as indicated by the boxes in each graph. ATP was included throughout the experiments in the i.o mode. b Concentration-dependent effect of H2O2. Normalized channel activity was plotted against concentration of H2O2. Data (n = 4–6) were fitted with a combined Hill’s equation as: , where [H2O2] was the concentration of H2O2, A the extent of facilitation, Kdf and Kdi apparent dissociation constants, and n f and n i Hill’s numbers for facilitation and inhibition, respectively. The fitted curve was drawn with A = 147, Kdf = 0.68 mM, n f = 2, Kdi = 3.11 mM, and n i = 3 (r 2 = 0.983). d Summary of the normalized channel activity in the presence of CaM + ATP in i.o. mode before and after addition of H2O2 ± KN-93 (n = 5–6). Data are shown as mean ± SE. *P < 0.05 versus CaM (t test), NS not significant (ANOVA)
