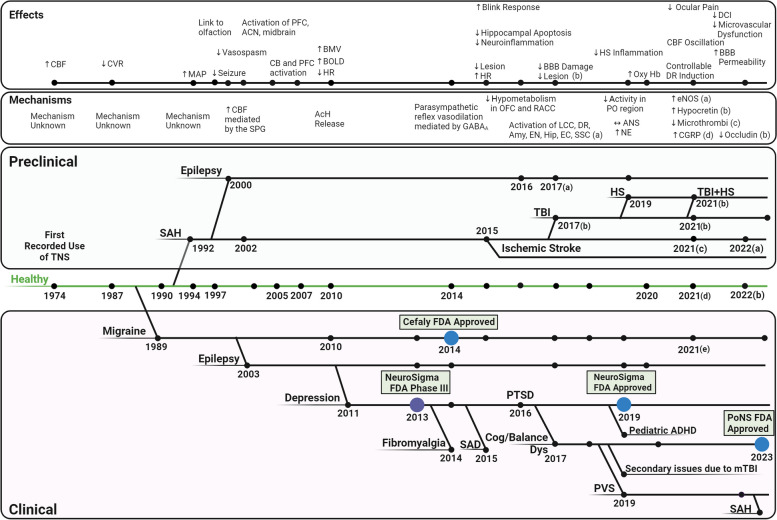
Fig. 1.
A brief history of Trigeminal Nerve Stimulation. TNS was first used in 1974 to assess the neural control of cerebral blood flow. Since then, it has been applied clinically in migraine, epilepsy, depression, PTSD, fibromyalgia, SAD, cognitive/balance dysfunction, pediatric ADHD, PVS, SAH, and secondary issues due to mTBI. In 2014, Cefaly was approved by the FDA for treatment of migraine, Neurosigma was approved in 2019 for pediatric ADHD, and PoNS was approved in 2023 for cognitive/balance dysfunction. Preclinically, the efficacy of TNS has additionally been assessed in TBI, HS, TBI + HS, and ischemic stroke. In the past decade, the effects and mechanisms of TNS within the brain and throughout the body have been expanded upon. (This figure was generated using BioRender.com) (AcH: acetylcholine: ACN: anticorrelated networks; ADHD: attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder; ANS: autonomic nervous system; BBB: blood–brain barrier; BOLD: Blood Oxygenation Level Dependent; CB: cingulum bundle; CBF: cerebral blood flow; CGRP: Calcitonin gene-related peptide; CVR: cerebrovascular resistance; HR: heart rate; HS: hemorrhagic shock; mTBI: mild traumatic brain injury; PFC: prefrontal cortex; PTSD: post-traumatic stress disorder; PVS: persistent vegetative state; SAD: social anxiety disorder; SAH: subarachnoid hemorrhage; TBI: traumatic brain injury; TNS: trigeminal nerve stimulation;)