Fig. 3.
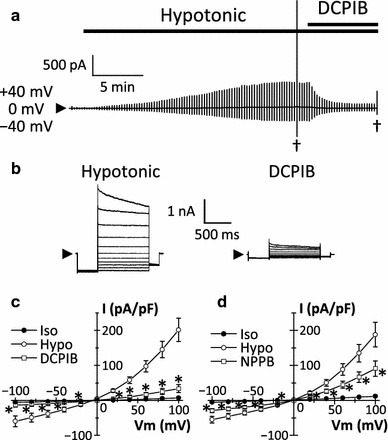
Effects of Cl− channel blockers on swelling-activated Cl− currents in MCE301 cells. a Representative swelling-activated Cl− currents before and during the application of 2.5 µM 4-(2-butyl-6,7-dichloro-2-cyclopentylindan-1-on-5-yl)oxybutyric acid (DCPIB). Alternating pulses of ±40 mV and step pulses from −100 to +100 mV in 20-mV increments (with a pre-pulse to −100 mV and a post-pulse to −60 mV) were applied from a holding potential of 0 mV. Daggers Time points at which step pulses were applied, arrowhead the zero current level. b Expanded traces of current responses to step pulses before (left) and during (right) DCPIB application. c Instantaneous I–V relationships of swelling-activated Cl− currents in the absence and presence of DCPIB. Each data point represents the mean ± SEM (vertical bar) of four experiments, *P < 0.05 compared to swelling-activated Cl− currents in the absence of DCPIB. d Instantaneous I–V relationships of swelling-activated Cl− currents in the absence and presence of 10 µM 5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino)benzoic acid (NPPB). Each data point represents the mean ± SEM (vertical bar) of seven experiments. *P < 0.05 compared to swelling-activated Cl− currents in the absence of NPPB. Iso Isotonic, Hypo hypotonic
