Fig. 1.
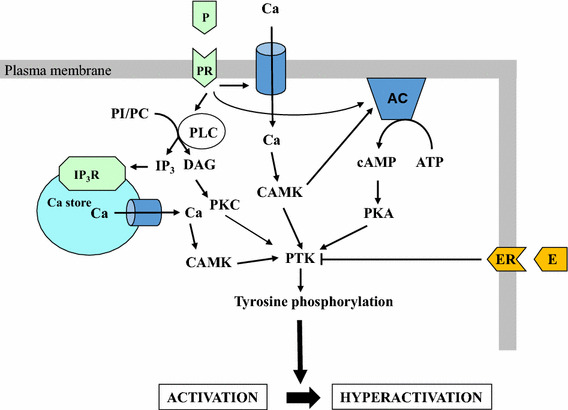
Hypothesized mechanism for the regulation of hyperactivation enhancement by progesterone and estradiol. AC adenylate cyclase, ATP adenosine triphosphate, CAMK calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, cAMP cyclic adenosine monophosphate, DAG diacylglycerol, E estradiol, ER estrogen receptor, IP 3 inositol 1,4,5-tris–phosphate, IP 3 R inositol 1,4,5-tris–phosphate receptor, P progesterone, PC phosphatidylcholine, PI phosphatidylinositol, PKA protein kinase A, PKC protein kinase C, PLC phospholipase C, PR progesterone receptor, PTK protein tyrosine kinase
