Fig. 5.
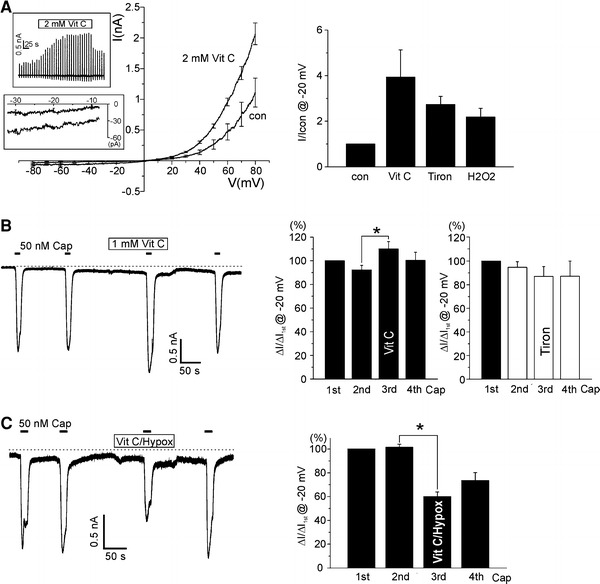
Effects of vitamin C and tiron on TRPV1 and I TRPV1,Cap. a Summary of I–V curves in response to 2 mM vitamin C in HEK293T cell expressing TRPV1 (n = 4, left panel). Current traces were obtained from the ramp-like pulses (upper inset), and the amplitudes of inward current at −20 mV were measured (lower inset, vertical expansion of I–V curve). The bar graphs in right panel shows summary of the currents measured at −20 mV and their increase by vitamin C (n = 4), tiron (100 μM, n = 7), and H2O2 (n = 5). For comparison, the amplitudes of inward current at −20 mV were normalized to the control in each cell. b Representative current trace at −20 mV holding voltage showing the repetitive activation of TRPV1 by 50 nM capsaicin (horizontal bars). 1 mM vitamin C was applied before the third stimulus of capsaicin, which augmented I TRPV1,Cap (left panel). Summary of the capsaicin-induced inward currents normalized to the first response. I TRPV1,Cap was increased by vitamin C pretreatment (n = 14, middle panel) while not changed by tiron pretreatment (n = 14, right panel). c Effects of vitamin C on the hypoxic inhibition of I TRPV1,Cap. Vitamin C was applied together with hypoxia (Vit C/Hypox) before the third application of 50 nM capsaicin. Both the increase of basal inward current and the suppression of I TRPV1,Cap by hypoxia was observed. Summary of the capsaicin-induced inward currents normalized to the first response (n = 20, right panel)
