Fig. 4.
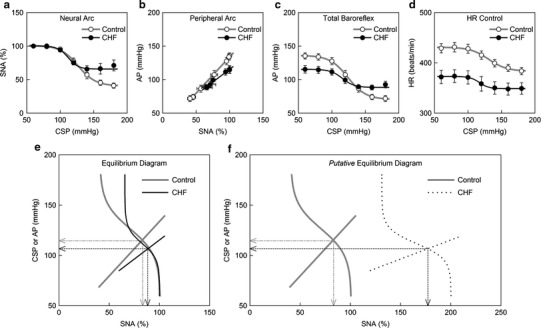
Static characteristics of the carotid sinus baroreflex averaged for the control (n = 12) and chronic heart failure (CHF; n = 7) rats. a Static characteristics of the baroreflex neural arc. An increase in CSP decreases SNA. The response range in SNA is significantly attenuated in CHF. b Static characteristics of the baroreflex peripheral arc. An increase in SNA increases AP in a linear manner. The slope of the regression line is significantly gentler in CHF. c Static characteristics of the total baroreflex. CSP and AP show an inverse sigmoidal relationship. The response range of AP and the maximum gain are significantly smaller in CHF. d Static characteristics between CSP and HR. CSP and HR show an inverse sigmoidal relationship. The response range of HR and the minimum HR are significantly smaller in CHF. e Baroreflex equilibrium diagram constructed from the fitted logistic function for the neural arc and the regression line for the peripheral arc. f Putative baroreflex equilibrium diagram in which the SNA axis is scaled so that the maximum absolute SNA in CHF becomes two times higher than that in control. In panels e and f, the dotted lines with arrowheads indicate the operating-point AP and SNA in CHF. The dash-dot lines with arrowheads indicate the operating-point AP and SNA in control
