Fig. 5.
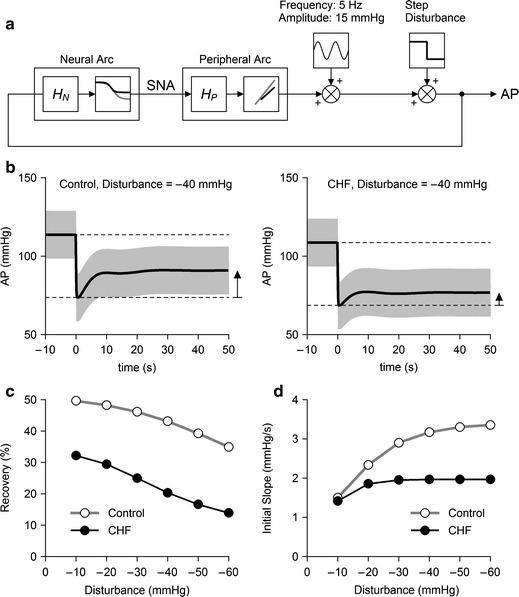
a Block diagram for the simulation of AP regulation. HN and HP represent dynamic characteristics of the neural and peripheral arcs, respectively. The static characteristics of the neural arc were modeled as a logistic function. The static characteristics of the peripheral arc were modeled as a straight line. Parameters for the logistic function and the regression line were derived from mean values shown in Table 3. A 5-Hz sine wave with an amplitude of 15 mmHg was added to mimic pulsatile pressure. Exogenous step disturbances ranging from −10 to −60 mmHg were applied, and the closed-loop AP responses were calculated for control and CHF conditions. b Typical simulation results during an exogenous pressure disturbance of −40 mmHg. The pulsatile pressure is shown in gray, and mean AP signal is shown as a bold line. The horizontal dotted lines indicate the mean AP values just before and after the onset of step disturbance. AP recovers less efficiently in the CHF simulation compared to the control simulation. c Percent recovery of AP as a function of the size of disturbance. d The initial slope of the recovery as a function of the size of disturbance
