Fig. 1.
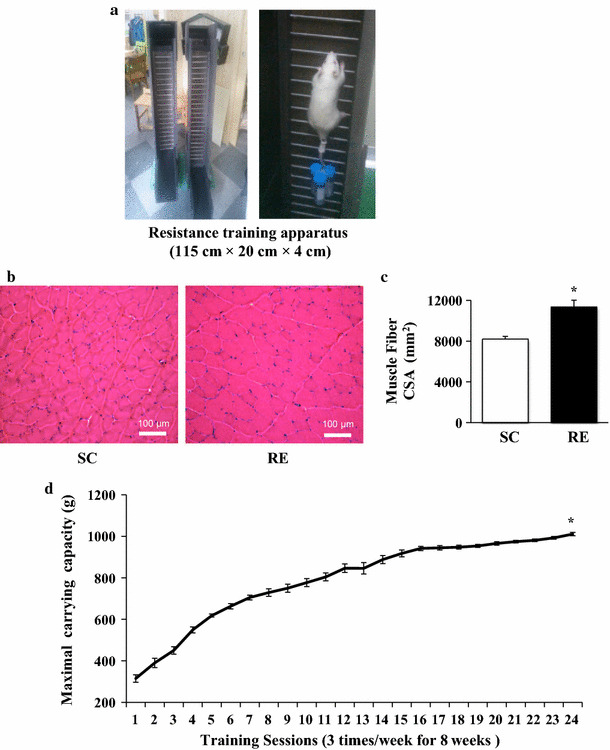
Long-term resistance exercise induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy and reinforces muscle strength. a Resistance training apparatus (width × length × gap = 115 cm × 20 cm × 4 cm). b Left Histological cross section of the flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) muscle in sedentary control group (SC), Right Histological cross section of the FDP muscle in resistance exercise group (RE). c Cross-sectional area (CSA) of FDP muscle fiber in SC and SE. Each bar represents the mean ± SE for the FDP muscles. Asterisks indicate significant differences between the two groups (*p < 0.01). d Maximal carrying capacity per each session for total training sessions. Asterisks denote significant difference in carrying capacity between the baseline and final carrying weight (*p < 0.01). The final carrying capacity (1011 g ± 8.1) was increased up to approximately 3.2-fold compared to baseline (315 g ± 17.8). Smooth marked scatters were represented as mean ± SE (n = 10). An asterisk indicates significant difference in RE groups (*p < 0.01)
