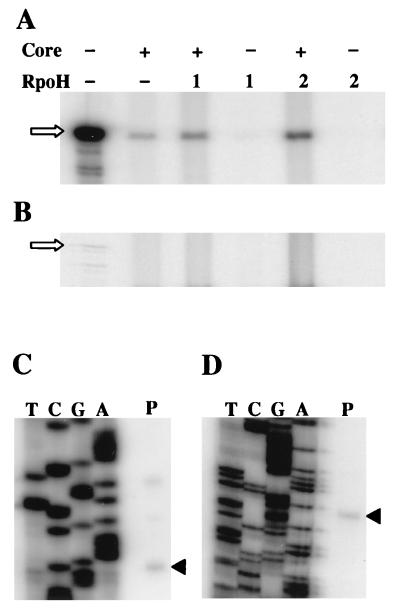
FIG. 6.
Transcription of the B. japonicum groESL1 promoter and the dnaKJ promoter by B. japonicum RNA polymerase reconstituted with purified RpoH factors. (A) Transcription of the B. japonicum groESL1 promoter. The enzyme combinations tested are indicated. Core, B. japonicum RNA polymerase core enzyme; RpoH, purified RpoHHis protein. The arrow points to an RNA size marker of 406 nucleotides. (B) Transcription of the B. japonicum dnaKJ promoter. The enzyme combinations are as indicated in panel A. (C) Primer extension analysis of in vitro-synthesized groESL1 transcript. Oligonucleotide 702 was used for the sequencing (TCGA) and primer extension reaction. The triangle points to the start site, which has been determined in vivo (2). The origin of small amounts of slower-migrating bands is not known because corresponding products were not observed after in vitro transcription. (D) Primer extension analysis of in vitro-synthesized B. japonicum dnaKJ transcript. Oligonucleotide DnaK12 was used for the sequencing (TCGA) and primer extension reaction. The 5′ end of the reverse transcript (indicated by a triangle) corresponds to the major start site found in vivo (16).