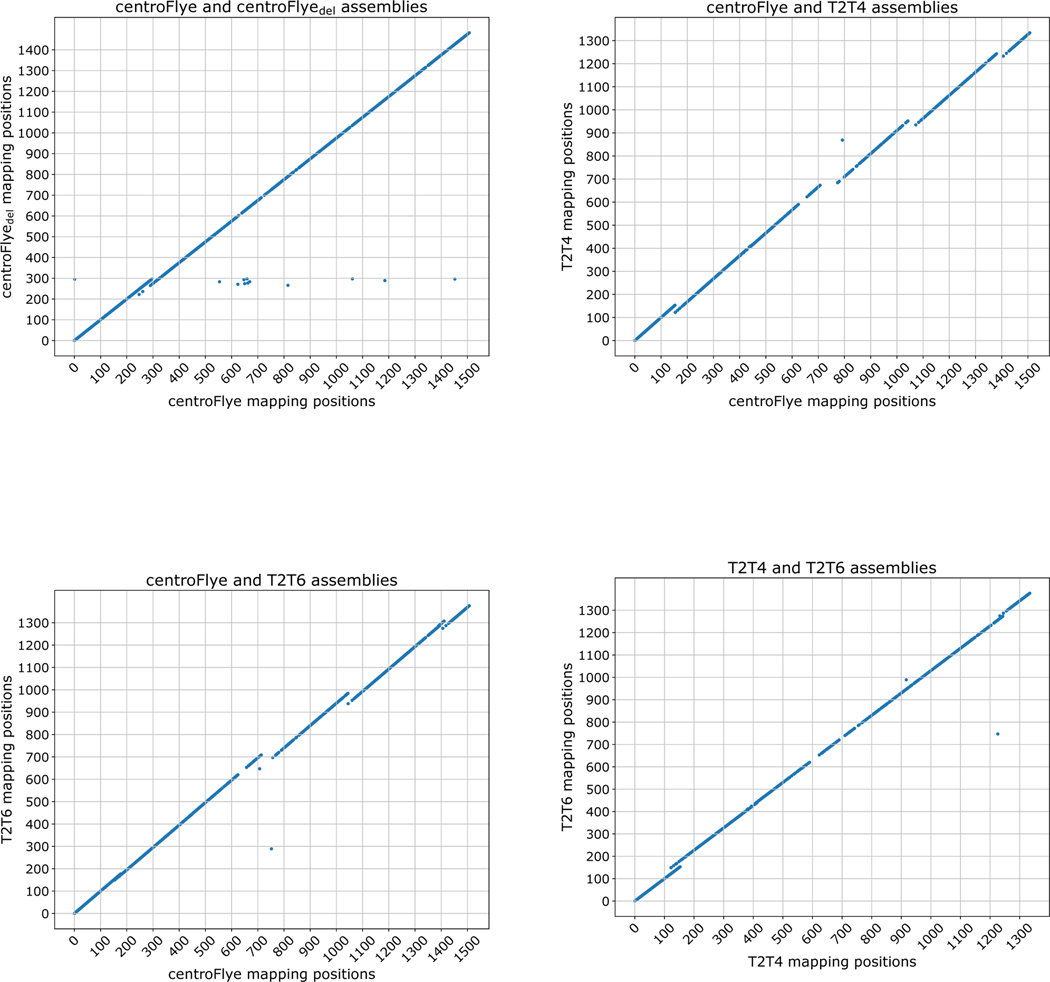
Figure 4. Comparison of read mappings between the centroFlye, centroFlyedel, T2T4, and T2T6 assemblies.
Each dot corresponds to a centromeric read. X- and Y-coordinate represent the starting unit position in the corresponding assemblies. (Top Left) Comparison of centroFlye and centroFlyedel assemblies reveals a discrepancy around unit 300 — 25 units deletion in the centroFlyedel assembly. (Top Right) Comparison of centroFlye and T2T4 assemblies reveals discrepancies around the following units in centroFlye (T2T4) assemblies: 150 (135) — 32 units deletion in T2T4, 450 (410) — 2 units deletion in T2T4, 750 (700) — 56 units deletion in T2T4, 1050 (950) — 47 units deletion in T2T4, and 1400 (1250) — 36 units deletion in the T2T4 in the centroFlye (T2T4) assembly. (Bottom Left) Comparison of centroFlye and T2T6 assemblies reveals discrepancies around the following units in centroFlye (T2T assemblies): 180 (175) — 5 units deletion in T2T6, 450 (445) — 1 units deletion in T2T6, 750 (720) — 56 units deletion in T2T6, 1050 (975) — 47 units deletion in T2T6, 1400 (1300) — 24 units deletion in T2T6. (Bottom Right) Comparison of T2T4 and T2T6 assemblies reveals discrepancies around the unit 150 and 1240 in both assemblies.