FIGURE 1.
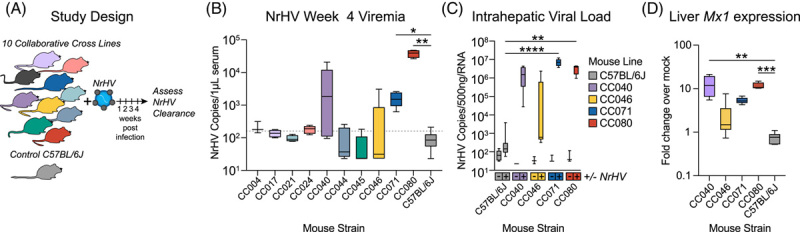
Host genetics is a determinant of acute hepacivirus clearance. (A) Study design. Ten Collaborative Cross (CC) strains and control C57BL/6J female mice 9–13 weeks in age were infected with 1 × 105 genome equivalents of recombinant NrHV or negative control PBS through retroorbital injection and bled weekly to monitor viremia. Mouse numbers per strain were: C57BL/6J N = 8, CC004 N = 4, CC017 N = 4, CC021 N = 4, CC024 N = 5, CC040 N = 5, CC044 N = 5, CC045 N = 5, CC046 N = 6. CC071 N = 5, CC080 N = 4. For all strains PBS mock infected N = 3. (B) Week 4 viremia as determined by qRT-PCR of viral RNA isolated from serum. The dotted line indicates the limit of quantitation. (C) Intrahepatic viral load 4 weeks after infection by qRT-PCR using 500 ng total liver RNA. Numbers of mice per group: C57BL/6J (8 NrHV, 4 Mock), CC040 (4 NrHV, 3 mock), CC046 (6 NrHV, 3 mock), CC071 (5 infected, 3 mock), CC080 (4 infected, 3 mock). (D) Mx1 intrahepatic gene expression 4 weeks by qRT-PCR using 500 ng total RNA. Data are expressed as fold change over mock infected by ∆∆CT method. For B and D, asterisks indicate statistical significance as determined by the Kruskal-Wallis test. For C, asterisks indicate statistical significance by 2-Way ANOVA with a Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. Abbreviations: CC, Collaborative Cross; NrHV, Norway rat hepacivirus.
