FIGURE 3.
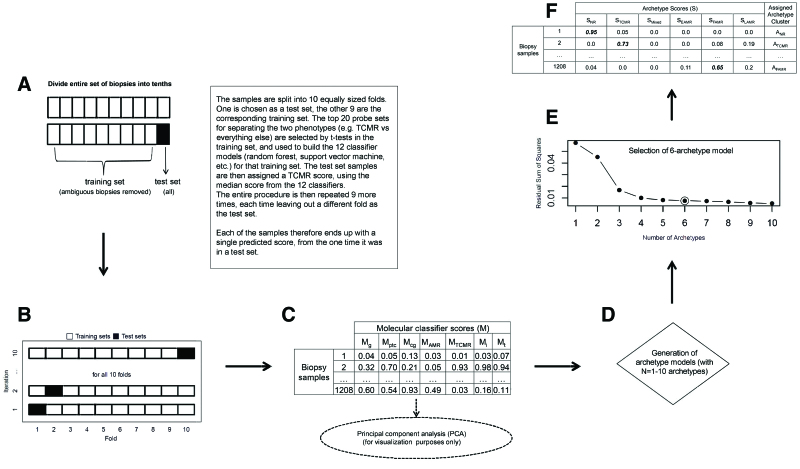
Classifier algorithm flowchart.60 A, Ten-fold cross-validation is illustrated, with each of the 10 folds shown as they are used in both the training and test sets. B and C, How the base classifiers (TCMR, AMR, i > 1, t > 1, g > 0, cg > 0, ptc > 0) were developed. For each of the 7 base classifiers: (B) 10-fold cross-validation is performed, randomly splitting the 1208 biopsies into 10 folds of equal or near-equal size. For each of 10 iterations, 1 fold is left out as a test set (black box), and a classifier is developed using the remaining 9 folds (white boxes) as the training set. All aspects of classifier development, including probe set selection, are carried out from scratch within the training set samples at each iteration. The top 20 (by P value) differentially expressed probe sets comparing the binary phenotypes within the training set are selected as input features for the classifier. Twelve different classifier algorithms are developed in each training set, generating 12 scores for each test set sample (1 for each classifier algorithm). The median of these 12 is used as each test set sample’s final score. This process is repeated over all 10 iterations, resulting in each biopsy being in a test set once and receiving a single value. C, This is repeated for each of the 7 base classifiers, resulting in a 1208 × 7 matrix of classifier test set scores. D–F, The archetypal analysis. These data are used as the input for both the principal component analysis (used for visualizing the multivariate distribution) and the archetypal analysis. D, We generated 10 archetype models (with n = 1–10 archetypes). The residual sum of squares decreases with increasing numbers of archetypes (scree plot in E). We selected 6 archetypes (circled point in E) as the final archetypal model. F, All biopsy samples are assigned a score for each of the 6 archetypes, and cluster assignments are made based on the highest score within that biopsy. The tables included show what typical data look like but do not represent actual results. AMR, antibody-mediated rejection; cg, transplant glomerulopathy; EAMR, early-stage AMR; FAMR, fully developed AMR; g, glomerulitis; i, interstitial inflammation; LAMR, late-stage AMR; M, molecular classifier scores; NR, no rejection; ptc, peritubular capillaritis; S, archetype score; t, tubulitis; TCMR, T cell–mediated rejection.