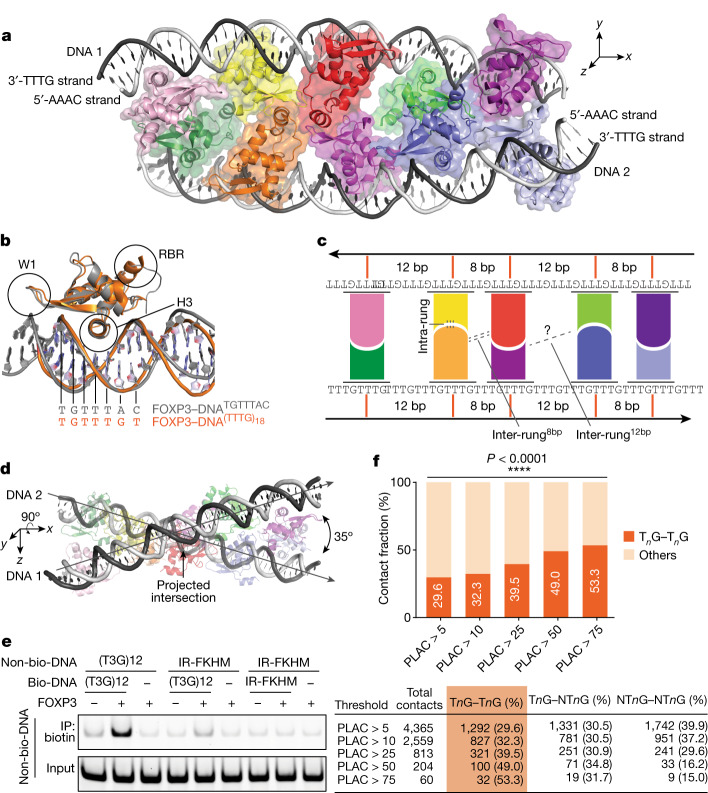
Fig. 2. FOXP3 forms a ladder-like multimer after binding to T3G repeat DNA.
a, The cryo-EM structure of a FOXP3(∆N) decamer in a complex with two DNA molecules (grey) containing (T3G)18. Each of the ten FOXP3 subunits are coloured differently. b, Comparison of a representative FOXP3(∆N) subunit from a (orange) with a FOXP3(∆N) subunit from the head-to-head dimeric structure (grey; Protein Data Bank (PDB): 7TDX). H3 recognizes the DNA sequence (TGTTTAC in the head-to-head dimer, TGTTTGT in the ladder-like multimer) by inserting it into the major groove. c, Schematic of the ladder-like architecture of FOXP3 on T3G-repeat DNA. d, The skew relationship between the two DNA molecules, which is evident when looking down the y axis of a. e, DNA-bridging assay. Biotinylated DNA (bio-DNA, 82 bp) and non-biotinylated DNA (non-bio-DNA, 60 bp) were mixed at a 1:1 ratio (0.1 μM each), incubated with FOXP3(∆N) (0.4 μM) and processed for Streptavidin pull-down before gel analysis. Non-biotinylated DNA in the eluate was visualized by SybrGold staining. f, Chromatin contacts at FOXP3-bound anchors identified using Hi-C-seq and PLAC-seq12. Contacts with a frequency of >5 in the WT Treg cell Hi-C analysis and connected by two FOXP3-bound anchors were analysed with an increasing FOXP3 PLAC-seq count threshold. The percentage of the unique contacts mediated by two TnG anchors (out of all unique contacts between two FOXP3-bound anchors) is indicated. All TnG–TnG contacts were between two distinct 10 kb anchor bins. NTnG, non-TnG.