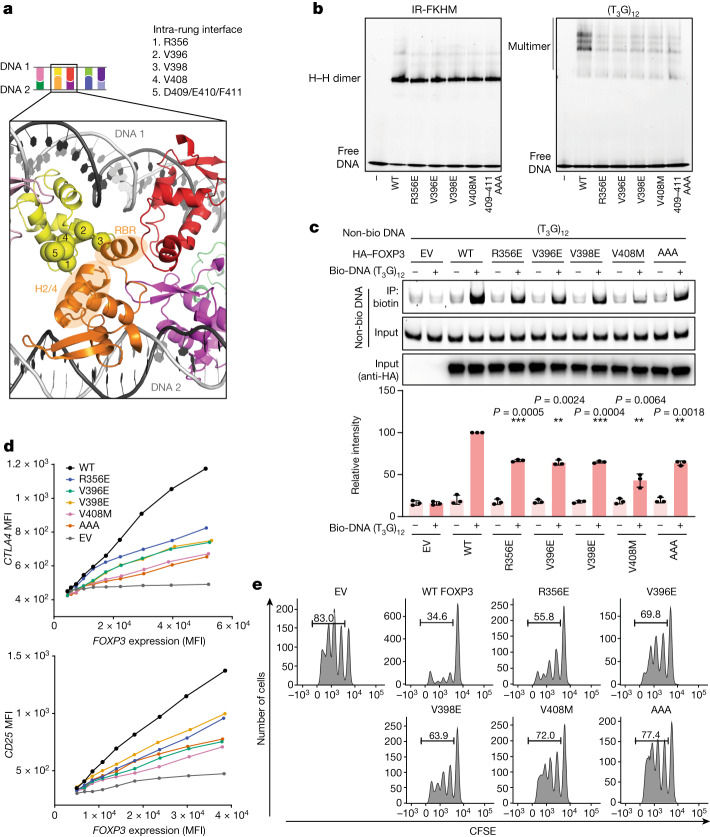
Fig. 3. Intra-rung interactions are essential for TnG repeat recognition, DNA bridging and the cellular functions of FOXP3.
a, The intra-rung interface. The α-carbons of Arg356, Val396, Val398, Val408 and Asp409/Glu410/Phe411 are shown as spheres. These residues on the yellow subunit interact with RBR and H2/H4 loop of the orange subunit. The subunit colours are as described in Fig. 2a. b, The effect of intra-rung interface mutations on DNA binding. MBP-tagged FOXP3(∆N) (0.4 μM) was incubated with IR-FKHM or (T3G)12 (60 bp for both) and analysed using a native gel shift assay. c, The effect of intra-rung interface mutations on DNA bridging. FOXP3 (or empty vector (EV)) was expressed in HEK293T cells and the lysate was incubated with a mixture of biotinylated and non-biotinylated DNA (1:1 ratio) and then analysed using Streptavidin pull-down and gel analysis. The relative levels of non-biotinylated DNA co-purified with biotinylated DNA were quantified from three independent pull-downs. The difference was compared with the WT in the presence of biotinylated DNA. Statistical analysis was performed using two-tailed paired t-tests; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.005. d, Transcriptional activity of FOXP3. CD4+ T cells were retrovirally transduced to express FOXP3, and its transcriptional activity was analysed by measuring the protein levels of the known target genes CTLA4 and CD25 using fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). FOXP3 levels were measured on the basis of Thy1.1 expression, which is under the control of IRES, encoded by the bicistronic FOXP3 mRNA. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. e, T cell suppression assay of intra-rung interface mutations. FOXP3-transduced T cells (suppressors) were mixed with naive T cells (responders) at a 1:2 ratio and the effect of the suppressor cells on the proliferation of the responder cells was measured on the basis of the carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE) dilution profile of the responder T cells.