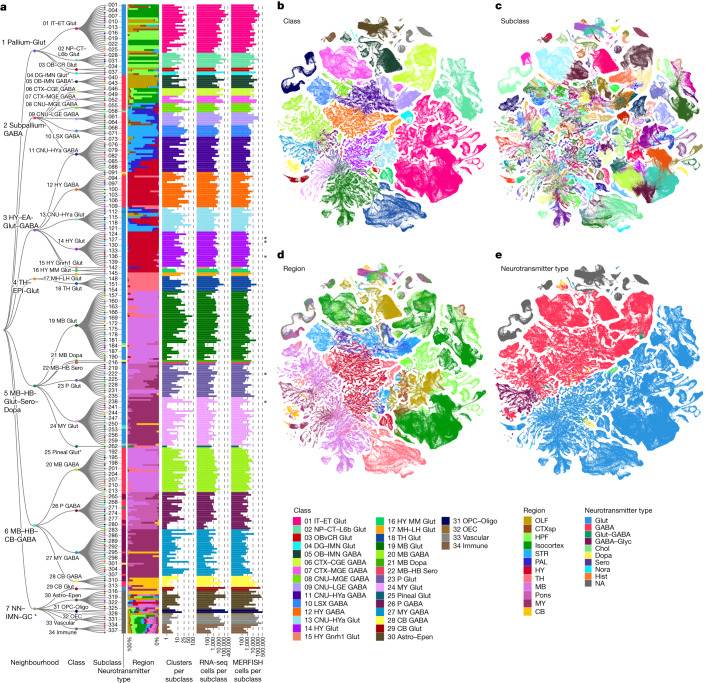
Fig. 1. Transcriptomic cell-type taxonomy of the whole mouse brain.
a, Left, the transcriptomic taxonomy tree of 338 subclasses organized in a dendrogram (10xv2: n = 1,699,939 cells; 10xv3: n = 2,341,350 cells; 10x Multiome: n = 1,687 nuclei). The neighbourhood and class levels are marked on the taxonomy tree. Classes marked with asterisks are included in the NN–IMN-GC neighbourhood. The IDs of every third subclass are shown to the right of the dendrogram. Full subclass names are provided in Supplementary Table 7. Following subclass IDs, bar plots represent (left to right): major neurotransmitter type, region distribution of profiled cells, number of clusters per subclass, number of RNA-seq cells analysed per subclass, and number of cells analysed by MERFISH per subclass. Subclasses marked with grey dots contain sex-dominant clusters. Sex-dominant clusters within a subclass are identified by calculating the odds and log P value for male/female distribution per cluster. Clusters with odds < 0.2 and log10(P value) < −10 are considered to be sex-dominant. b–e, UMAP representation of all cell types coloured by class (b), subclass (c), brain region (d) and major neurotransmitter type (e). Colour schemes for a–e are shown in the key at the bottom right of the figure. Astro, astrocyte; CB, cerebellum; CGE, caudal ganglionic eminence; CNU, cerebral nuclei; CR, Cajal–Retzius; CT, corticothalamic; CTX, cerebral cortex; CTXsp, cortical subplate; DG, dentate gyrus; EA, extended amygdala; Epen, ependymal; EPI, epithalamus; ET, extratelencephalic; GC, granule cell; HB, hindbrain; HPF, hippocampal formation; HY, hypothalamus; HYa, anterior hypothalamic; IMN, immature neurons; IT, intratelencephalic; L6b, layer 6b; LGE, lateral ganglionic eminence; LH, lateral habenula; LSX, lateral septal complex; MB, midbrain; MGE, medial ganglionic eminence; MH, medial habenula; MM, medial mammillary nucleus; MY, medulla; NN, non-neuronal; NP, near-projecting; OB, olfactory bulb; OEC, olfactory ensheathing cells; OLF, olfactory areas; Oligo, oligodendrocytes; OPC, oligodendrocyte precursor cells; P, pons; PAL, pallidum; STR, striatum; TH, thalamus. Neurotransmitter types: Chol, cholinergic; Dopa, dopaminergic; GABA, GABAergic; Glut, glutamatergic; Glyc, glycinergic; Hist, histaminergic; Nora, noradrenergic; Sero, serotonergic; NA, not applicable (no neurotransmitter detected).