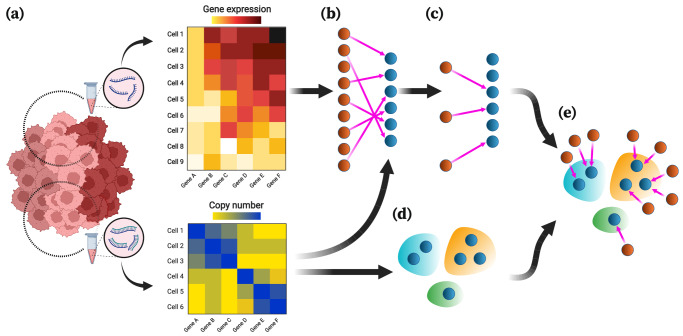
Fig. 1. Overview of MaCroDNA.
a The input of MaCroDNA consists of the scRNA-seq gene expression read count tables (or their log-transformed values) and the scDNA-seq absolute copy numbers (or their log-transformed values) that are supposedly obtained from the same tissue. Distinct clones are distinguished by color saturation. b Given the gene expression and copy number matrices (intensity of pixel colors is proportional to copy number/gene expression values), MaCroDNA identifies the assignment of the scRNA-seq cells (dark orange circles) with gene expression values to the scDNA-seq cells (dark blue circles) with copy number values. When the number of the scRNA-seq cells is higher than the number of the scDNA-seq cells (as in the above example), MaCroDNA infers the correspondence between the cells (shown by pink arrows) by solving a series of maximum weighted bipartite matching problems (in this example, two steps are required). In the first step, only six scRNA-seq cells (equal to the number of the scDNA-seq cells) are assigned to the scDNA-seq cells such that no two scRNA-seq cells are paired with the same scDNA-seq cell, and the sum of the Pearson correlation coefficients between the pairs is maximized. c The scRNA-seq cells whose correspondences were identified in the last step are removed. Next, the remaining three scRNA-seq cells are assigned to the best scDNA-seq cells in a one-to-one fashion according to the same correlation-based criterion. d The clones are inferred from the scDNA-seq data using an algorithm of choice (the clones are represented by blue, orange, and green bubble shapes). e Given the cell-to-cell correspondences and the clonal assignment of the scDNA-seq cells, we can assign the scRNA-seq cells to the scDNA-seq clones. The clonal assignment of a scRNA-seq cell is that of its corresponding scDNA-seq cell. This figure was created with BioRender.com.