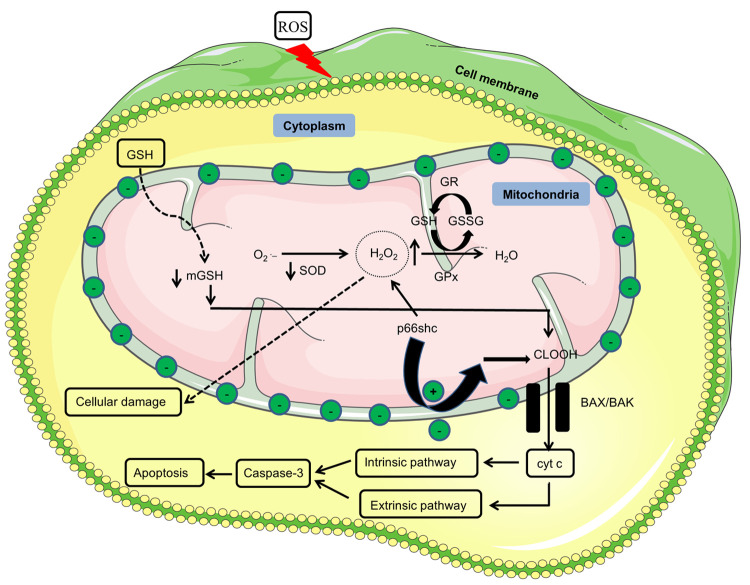
Figure 2.
| Mitochondria functionality. Reduced GSH due to ROS is translocated into the mitochondria, where it acts as a cofactor for GPx for the conversion of hydrogen peroxide into water. Due to reduced levels of GSH, H2O2 keeps on accumulating in the mitochondria, which diffuses from the mitochondria and starts causing cellular damage. Adaptor protein p66shc under stress conditions translocates into the mitochondria and starts producing H2O2 on its own in the absence of superoxide dismutase, which further leads to higher levels of H2O2. Stress conditions generated due to lower mitochondrial glutathione levels cause the oxidation of the cardiolipin–cytochrome c complex. As a result, cytochrome c diffuses through the mitochondria via BAX/BAK created pores and starts the apoptosis via caspase-3. P66shc also reduces the membrane potential to release cyt c into the cytosol. Upper head arrows show increased expression, while lower head arrows represent a decreased expression. Green circles with negative symbol represents membrane negative potential whereas green circles with plus symbol presents reduction in the membrane potential. O2•–, superoxide; SOD, superoxide dismutase; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, glutathione disulfide; CLOOH, oxidized cardiolipin; BAX, B-cell lymphoma-2(Bcl-2)-associated X protein; BAK, Bcl-2 antagonist/killer; cty c, cytochrome c; p66shc, 66 kDa adaptor protein and member of the Src homologous-collagen homologue.