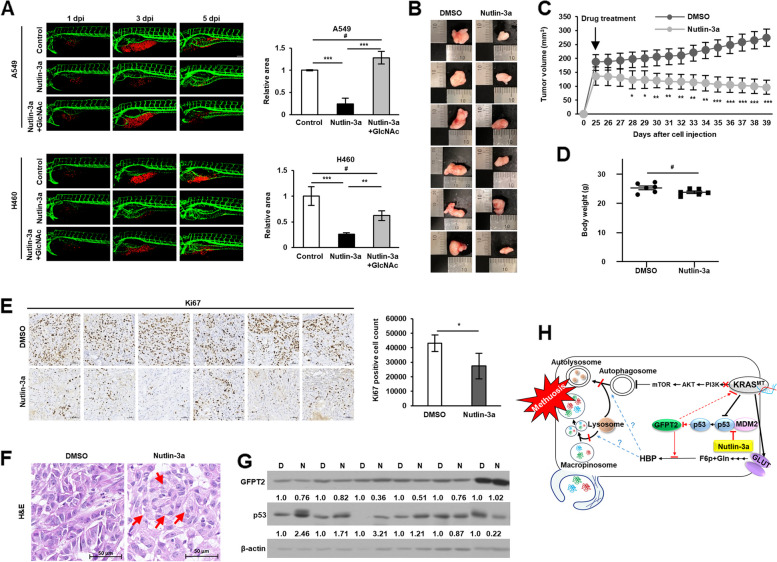
Fig. 8.
Anticancer effects of nutlin-3a confirmed in vivo. A Representative confocal images of CM-Dil-labeled cancer cells (red) and vasculature (green) in zebrafish larvae (left). Quantified data show cancer cell volume after nutlin-3a treatment and GlcNAc co-treatment compared with that of the control group (right). Supplement of GlcNAc-rescued cancer cell volume reduces after nutlin-3a treatment. B, C Images (B) and comparison (C) of growth rates of subcutaneous tumors formed by A549 injection; tumor growth is observed in the presence or absence of nutlin-3a. D Weight of mice after treatment with either vehicle control or nutlin-3a on the day of euthanasia. E Immunohistochemical analysis of Ki67 expression in tumor tissues. F Vacuole examination in H&E stained tumor tissues. Red arrows indicate vacuoles. G Western blot analysis of GFPT2 and p53 expression in in vivo xenograft tumors. The densitometry quantification of the western blot was determined using Image J software (Ver. 1/52n, NIH). H Proposed mechanism of nutlin-3a-induced methuosis-like cell death. Scale bar: 20 μm for (A) and 50 μm for (E, F). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation; n = 6. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with control