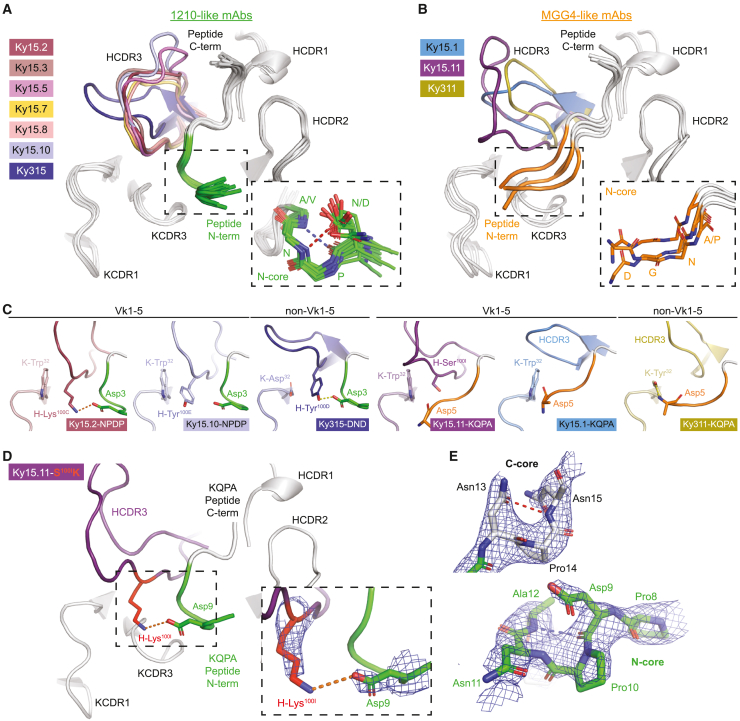
Figure 4.
HCDR3 sequence and orientation of VH3-33 mAbs influence peptide N-core conformation
(A and B) X-ray crystal structures of seven 1210-like mAbs (A) and three MGG4-like mAbs (B) bound to various peptides, with C-core colored gray and N-core shown in green (A) or orange (B). HCDR1s, HCDR2s, KCDR1s, and KCDR3s are shown in gray, and HCDR3s are colored by mAb. The inset in (A) highlights the N-core type I β turn of the 1210-like binding conformation. The inset in (B) highlights the extended structure of the MGG4-like peptide N-core.
(C) HCDR3 features that influence the N-core conformation are shown for representative 1210-like mAbs (N-core colored green) and MGG4-like mAbs (N-core colored orange) with Vk1-5 or non-Vk1-5 KCs, as indicated. KCs are shown in paler colors for each mAb. Fab-peptide complexes and notable residues are labeled. Fab-peptide salt bridges and HBs are shown as orange and yellow dashed lines, respectively.
(D) X-ray crystal structure of Ky15.11-S100IK in complex with the KQPA peptide. Fab and peptide are colored as in (A), with mutated residue shown in red. The inset highlights the salt bridge (orange dashed line) between mutated H-Lys100I and peptide Asp9. Electron density associated with the salt bridging residues is shown as blue mesh.
(E) KQPA peptide bound by Ky15.11-S100IK is represented as sticks with residues labeled and corresponding electron density shown as blue mesh.
(A and E) Blue dashed lines indicate an intrachain HB between main-chain atoms, and red dashed lines indicate an intrachain HB mediated by side-chain atoms.
(D and E) Composite omit map electron density is contoured at 1.0 sigma.