Figure 1.
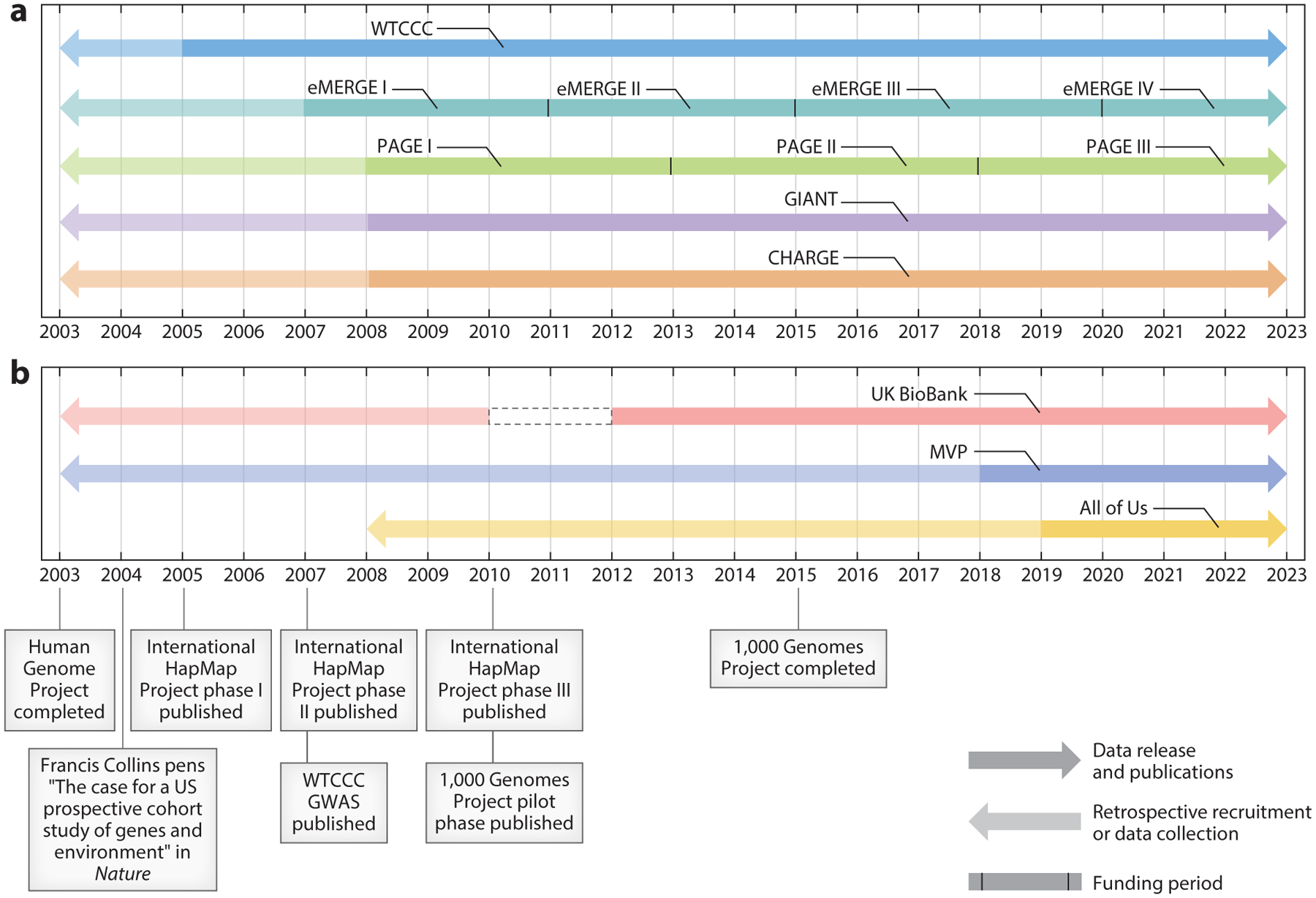
A timeline of the complicated evolution of GWAS consortia. This timeline is a snapshot of the formation of (a) select consortia that serve as the foundation of many contemporary GWAS and (b) newer large, prospective studies with genome-wide data that are fueling the next generation of GWAS consortia. The years on the x-axis represent a 20-year time frame within which we highlight some of the major pre-GWAS accomplishments that enabled the first and now commonplace GWAS. (a) The faded arrows pointing retrospectively represent studies within consortia that recruited participants or collected data prior to the years on the timeline (i.e., the 1958 British Birth Cohort). The black dividing markers represent the NIH funding periods for each iteration of the eMERGE and PAGE studies. While WTCCC is no longer aggregating new data from study investigators, we present this consortium as active since this dataset is one of many in the largest currently active consortium. Unlike WTCCC, GIANT and CHARGE are actively acquiring data to increase diversity and sample size. As such the forward arrows represent both the inclusion of new data and the use of these data in present-day GWAS. Similar to the forward pointing arrows in panel a, those in panel b also represent both data that are used in GWAS today and studies that are actively recruiting or collecting data. Abbreviations: CHARGE, Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology; eMERGE, Electronic Medical Records and Genomics; GIANT, Genetic Investigation of Anthropometric Traits; GWAS, genome-wide association study; NIH, National Institutes of Health; PAGE, Population Architecture using Genomics and Epidemiology; WTCCC, Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Figure adapted from images created with BioRender.com.
