Figure 1:
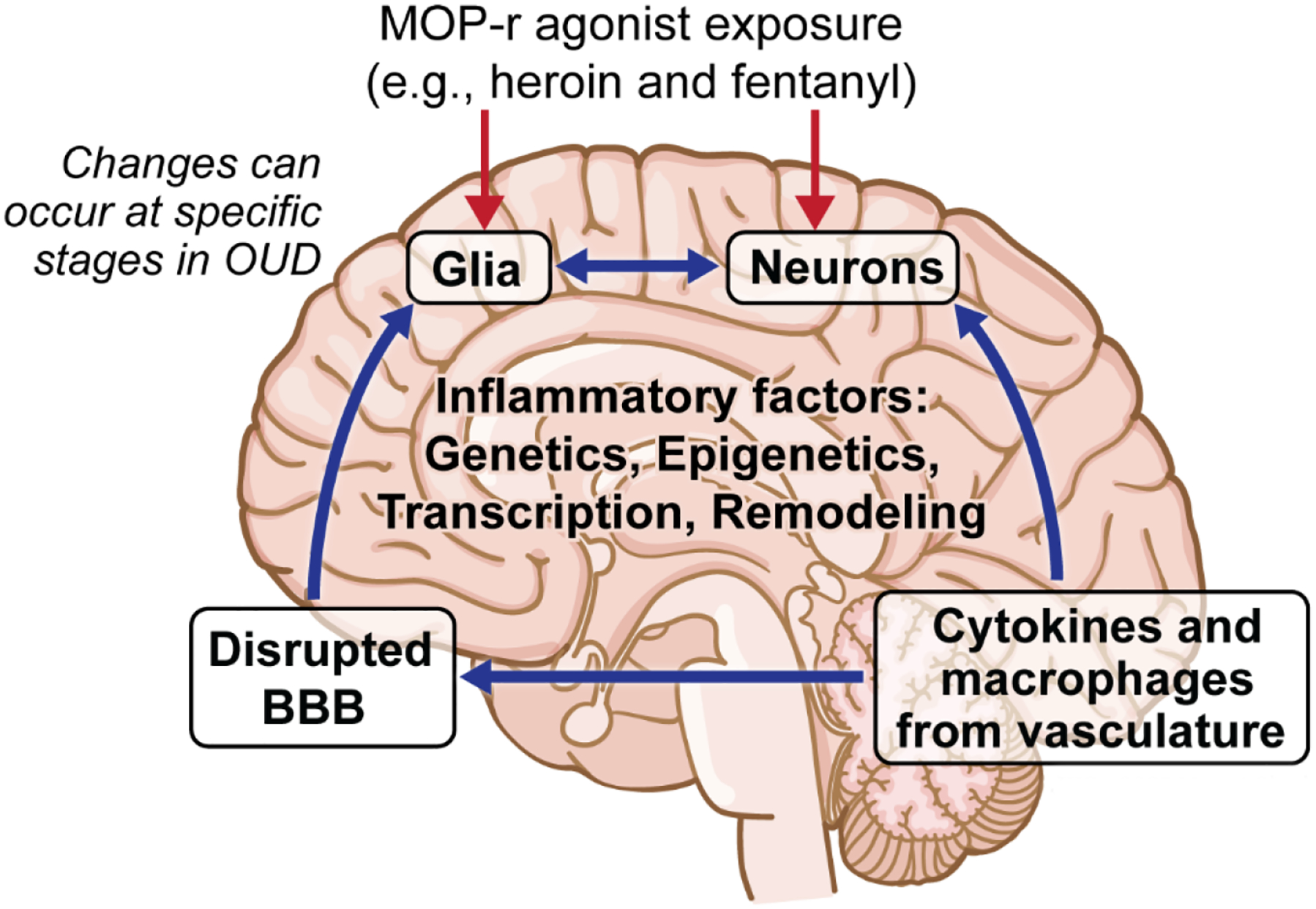
Schematic of major postulated immune interactions with CNS in persons with opioid use disorders (OUD). The four main interactive compartments affected in OUD can be summarized as 1) Neuronal populations in different parts of the brain, 2) Central glia that can functionally interact with neurons, 3) Changes in blood-brain barrier structure and function resulting in pathological permeability to peripheral macrophages cells and cytokines, and 4) Changes in peripheral immune cells and their release of soluble mediators, including cytokines.
