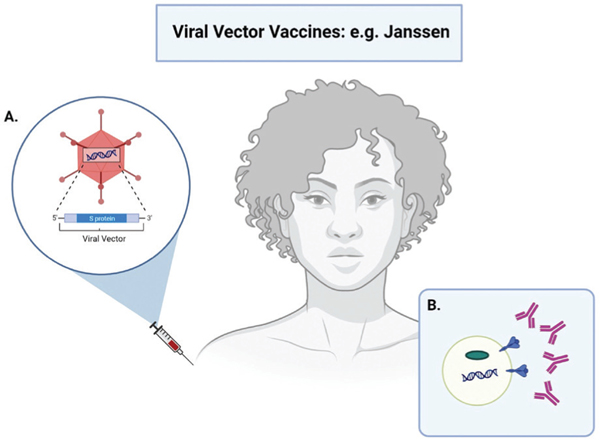
Figure 3.
Schematic overview of the working principle of viral vector vaccines to protect against COVID-19. A. A harmless non-coronavirus viral particle known as a vector is modified with the SARS-CoV-2 S protein DNA and injected intramuscular in the deltoid muscle of the shoulder. B. Production of the S protein antigen: the viral vector teaches the host cells to make copies of the S protein. This allows the host cell antibodies to recognize the spike protein if exposed to the virus. The host’s immune response is then similar to that of the mRNA vaccine, and is outlined in the caption of Figure 2. (created with BioRender.com)