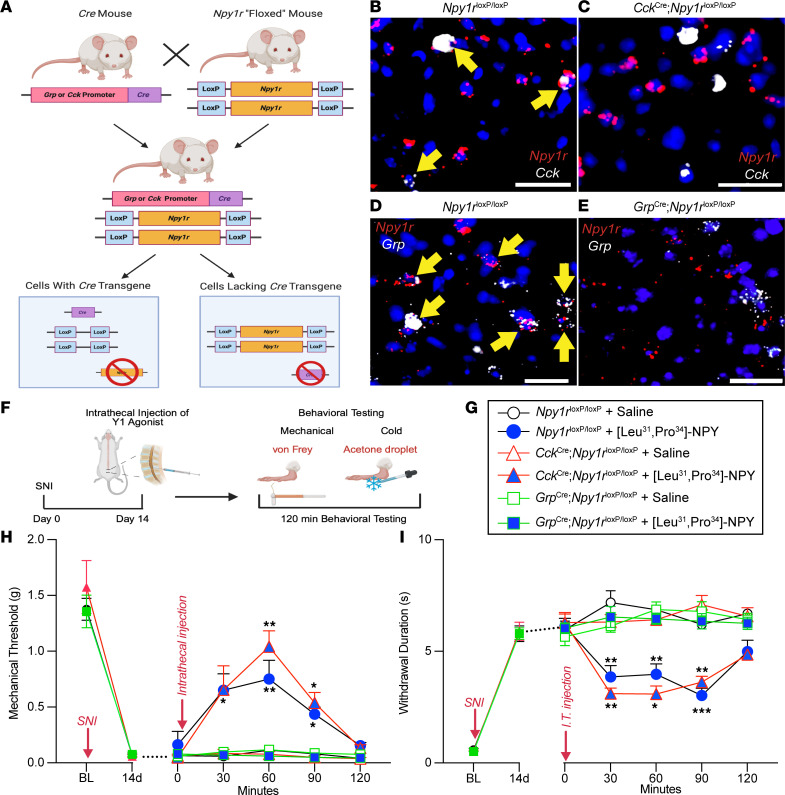
Figure 6. Grp/Npy1r-INs but not Cck/Npy1r-INs contribute to the inhibition of nerve injury–induced mechanical and cold allodynia by a Y1 agonist.
(A) Schematic representation of the conditional genetic knockout breeding protocol to delete Npy1r from CCK-Cre and GRP-Cre cells. (B–E) Confirmation of conditional deletion of Npy1r. FISH of sections of the lumbar spinal cord demonstrate that Npy1rloxP/loxP mice contain DH neurons that coexpress Npy1r and Cck as well as Npy1r and Grp. Conversely, Npy1rloxP/loxP CckCre mice lack expression of Npy1r in Cck-expressing neurons and Npy1rloxP/loxP GrpCre mice lack expression of Npy1r in Grp-expressing neurons. Yellow arrows indicate colocalization. Scale bars: 25 μm. (F) Experimental timeline for SNI, intrathecal pharmacology, and mechanical (von Frey) and cold (acetone droplet withdrawal) behavioral testing. (G) Genetic mouse lines and pharmacological drugs represented in H and I. (H) [Leu31, Pro34]-NPY abolishes SNI-induced mechanical allodynia in Npy1rloxP/loxP and Npy1rloxP/loxP CckCre mice but not in Npy1rloxP/loxP GrpCre mice (n = 8–9 mice/group). Three-way RM ANOVA: time × genotype × drug, F4,128 = 7.509, P < 0.0001; Tukey’s multiple-comparison tests. (I) [Leu31, Pro34]-NPY abolishes SNI-induced cold allodynia in Npy1rloxP/loxP and Npy1rloxP/loxP CckCre mice but not in Npy1rloxP/loxP GrpCre mice (n = 8–9 mice/group). Three-way RM ANOVA: time × genotype × drug, F4,128 = 6.322, P = 0.0001; Tukey’s multiple-comparison tests. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. Data shown as mean ± SEM.