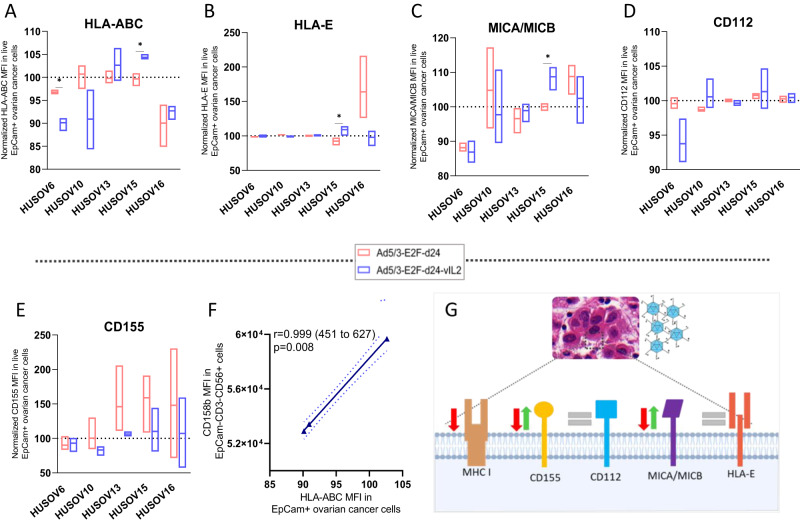
Fig. 4. Ad5/3-E2F-d24-vIL2 modulation of expression of proteins associated to NK cell engagement in ovarian cancer cells.
Differences on the expression of co-stimulatory and co-inhibitory proteins on the cancer cells surface for NK cell response were studied upon vIL-2 virus infection. Human ovarian cancer samples were plated in triplicates (2 × 105 cells/well), and after 24 h of incubation, samples were infected with Ad5/3-E2F-d24-vIL2 or Ad5/3-E2F-d24 virus, 100vp/cell. Cells were harvested after 48 h, and cancer cells were stained with live/dead cell dye (PI), EpCam, CD112, CD155, MICA/MICB, HLA-ABC, and HLA-E surface markers and cell fluorescence analysed by flow cytometry. Results were normalized to their respective mock (uninfected) group and presented as normalized percentages. A HLA-ABC, B HLA-E, C MICA/MICB, D CD112, and E CD155 MFI in ovarian cancer cells from patient samples HUSOV6, HUSOV10, HUSOV13, HUSOV15, and HUSOV16. F Correlation between the expression of CD158b MFI in NK+ cells and HLA-ABC MFI in ovarian cancer cells. G Schematic summarizing vIL-2 virus mediated changes on the expression of key ligands for NK cell response. Data sets were analysed for statistical significance by unpaired T test with Welch´s correction and presented as floating bars (min to max). *p < 0.05.