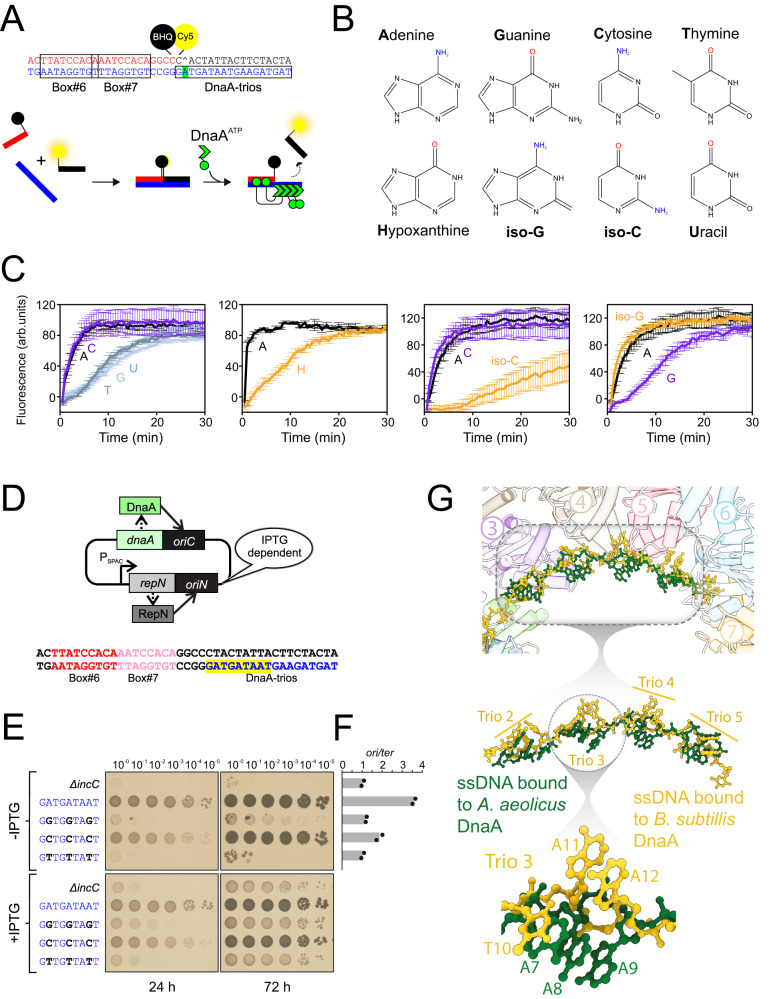
Fig. 4. The amine group on adenine mediates specificity for DnaA-trio recognition by DnaA.
A Schematic representation of BHQ strand separation assay. The fluorescently labelled oligonucleotide contains an abasic site complementary to the central adenine (base shown in green). B Structures of nucleobases used to replace adenine. C Strand separation assay performed with nucleotide substitutions at the central adenine of the first DnaA-trio, in the context of an abasic site at the complementary position. Positions of mutations and structure of modified bases are indicated. Data shows the average and percentage standard deviation from three independent experiments (source data are provided as a Source Data file). D Schematic of the inducible repN/oriN system used to bypass mutations affecting oriC activity in B. subtilis. Replication via oriN is turned on and off in the presence and absence of IPTG, respectively. E Spot titre analysis with strains that have replaced the central adenine of DnaA-trio#1-3. The presence or absence of IPTG indicates the induction state of the repN/oriN system. Wild-type (FDS682), ΔincC (FDS404), A→G (FDS688), A→C (FDS686), A→T (FDS691). F Marker frequency analysis of strains shown in panel F. Data shows the average and individual data points from two independent experiments (source data are provided as a Source Data file). G Comparison of ssDNA substrates from DnaA nucleoprotein complexes. The synthetic polyA ssDNA from A. aeolicus (shown in green) (PDB 3R8F) was superimposed onto the BUS ssDNA (shown in yellow). Insets provide greater detail of the distinct conformations adopted by the two ssDNA substrates.