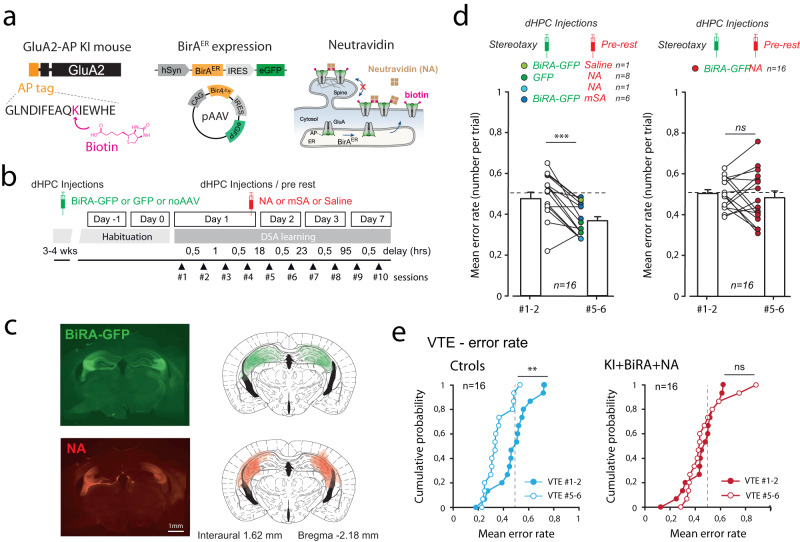
Fig. 6. An alternative AMPAR X-linking strategy allowing a better targeting of the CA3 area also induced complete forgetting of DSA rule.
a We recently developed a new strategy for AMPAR X-linking. Knock-in mice expressing endogenous AP-tagged GluA2 AMPAR subunits can be biotinylated in the presence of BiRAER, and once exported to the cell surface can be immobilized in the presence of external neutravidin (NA, cross-linking condition). b Similar in vivo pharmacological experiments as in Fig. 1d were performed, combining early stereotaxic dHPC injections of AAV-BiRA-GFP or AAV-GFP, and pre-rest injections of saline, mSA or NA. c Histological controls for the mSA and NA staining on top of the AAV-GFP expression. The combination of both injections better restrict AMPAR immobilization to the CA3 area. Template is from “the mouse brain” Paxinos and Franklin. d Mean error rates were compared between sessions #1–2 and sessions #5–6 to evaluate the retention of the DSA rule upon various pharmacological treatments (as indicated by color coding). Paired t-tests were used. ns not significant, ***p < 0.001. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. e The error rate in VTE runs was reported in sessions #1–2 (filled dots) and 5–6 (empty dots) for control (left) and cross-link (right) groups. t-tests were used. ns not significant. **p < 0.01. n = biologically independent animals.