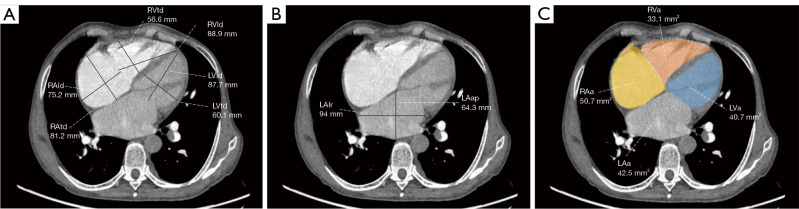
Figure 3.
Measurements of the diameters and areas in 4-chamber-view computed tomography pulmonary angiography. (A) The longest longitudinal and transverse diameters of the biventricles and right atrium are illustrated for reformatted 4-chamber views. The transverse axis is parallel to the line connecting the heart valves. The ventricle longitudinal line is the midpoint of the heart valve and the line connecting the apex of the heart, and the right atrium longitudinal line is perpendicular to the transverse axis. (B) The longest LAap and the widest LAlr are illustrated for reformatted 4-chamber views. The LAap is the largest straight-line distance connecting the front and back walls of the left atrium, and the LAlr is perpendicular to the LAap. (C) The maximum 4-chamber heart area was measured on the reformatted 4-chamber position. RVtd, transverse diameter of the right ventricle; LVtd, transverse diameter of the left ventricle; RVld, longitudinal diameter of the right ventricle; LVld, longitudinal diameter of the left ventricle; RAld, longitudinal diameter of the right atrium; RAtd, transverse diameter of the right atrium; LAlr, left-right dimension of the left atrium; LAap, anteroposterior dimension of the left atrium; RVa, area of the right ventricle; LVa, area of the left ventricle; RAa, right atrial area; LAa, left atrial area.