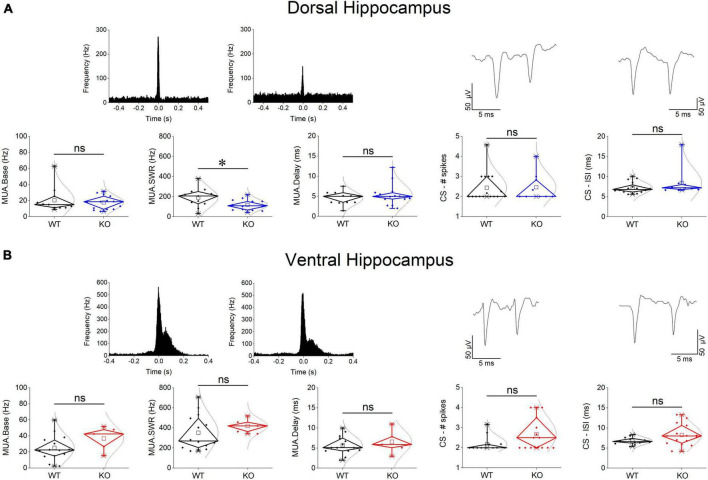
FIGURE 4.
Genotype effects on MUA and CSB in the dorsal (A) and the ventral hippocampus (B). Examples of MUA histograms triggered by the peaks of SPWs are shown on the top of MUA graphs. Examples of traces of CSB are shown on the top of the corresponding graphs of CSB. The results of statistical analysis (independent t-test) for the four variables are the following: MUA-Base: dorsal hippocampus t23 = 0.562, p = 0.58, WT = 11 rats, KO = 14 rats, and ventral hippocampus t17 = –1.43, p = 0.172, WT = 14 rats, KO = 5 rats; MUA-SWR: dorsal hippocampus t23 = 2.42, p = 0.024, WT = 11 rats, KO = 14 rats, and ventral hippocampus t–16.37 = –1.2, p = 0.247, WT = 14 rats, KO = 5 rats; MUA-Delay: dorsal hippocampus t23 = –0.884, p = 0.386, WT = 11 rats, KO = 14 rats, and ventral hippocampus t17 = –0.647, p = 0.526, WT = 14 rats, KO = 5 rats; CS-spikes: dorsal hippocampus t23 = –0.088, p = 0.931, WT = 16 rats, KO = 9 rats, and ventral hippocampus t20.612 = –2.07, p = 0.052, WT = 12 rats, KO = 15 rats; CS-ISI: dorsal hippocampus t23 = –1.224, p = 0.233, WT = 16 rats, KO = 9 rats, and ventral hippocampus t18.05 = –2.04, p = 0.056, WT = 12 rats, KO = 15 rats. Asterisk and “ns” denote statistically significant and not significant difference, respectively.