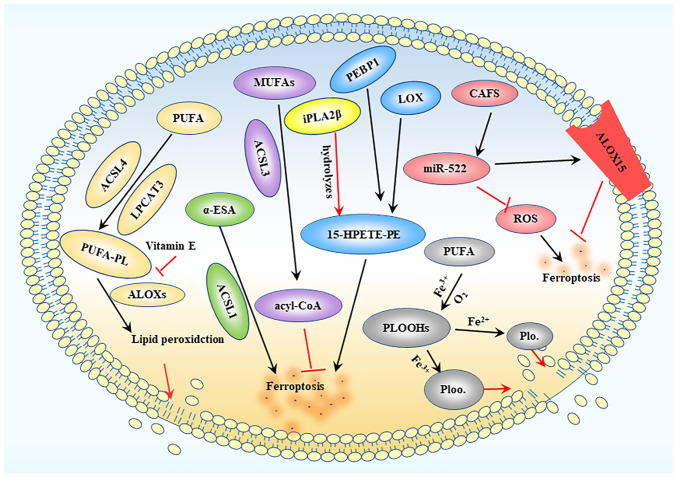
Figure 2.
Lipid peroxidation process. ACSL4 and LPCAT3 mediate PUFA binding to phospholipids to produce PUFA-PLs, while ALOXs further induce the production of lipid peroxides, ultimately destroying the lipid bilayer. MUFA is converted into acyl-CoA under the action of ACSL3, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis. LOX interacts with PEBP1 to produce 15-HPETE-PE, leading to ferroptotic death. CAFs produce extracellular vesicles containing miR-522, which can inhibit ROS accumulation and target ALOX15 to inhibit ferroptosis. ACSL, acyl-CoA synthetase long chain; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; PUFA-PL, PUFA phospholipid; MUFA, monounsaturated fatty acid; LOX, lipoxygenase; ALOX, arachidonic acid LOX; PEBP1, phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1; 15-HPETE-PE, 15-hydroperoxy-eicosa-tetraenoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine; CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; miR, microRNA; ROS, reactive oxygen species; PLOOH, phospholipid hydroperoxide; iPLA2β, calcium-independent PLA2β; α-ESA, α-eleostearic a.