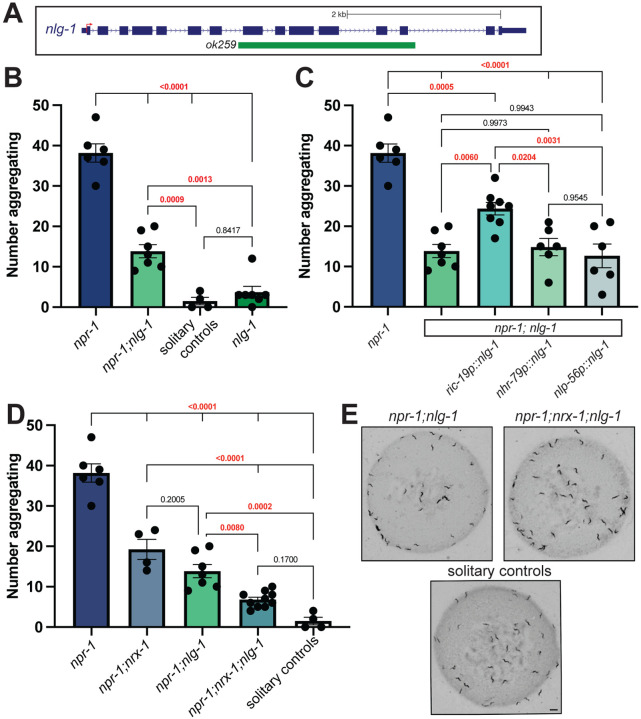
Fig. 3. NLG-1 contributes independent of NRX-1 in aggregation behavior.
A) Schematic of C. elegans nlg-1 gene showing deletion allele assessed. B) Graph showing number of aggregating animals in npr-1(ad609), npr-1(ad609);nlg-1(ok259), nlg-1(ok529), and solitary controls. nlg-1 deletion decreased aggregation behavior in npr-1 animals. C) Graph showing number of aggregating animals in npr-1(ad609);nlg-1(ok259) mutants with NLG-1 driven by ric-19, nhr-79, and nlp-56 promoters and controls. ric-19p expresses in all neurons, nhr-79p expresses in ADL and ASH sensory neurons and nlp-56p expresses in RMG neurons. D) Graph showing number of aggregating animals in npr-1(ad609), npr-1(ad609);nrx-1(wy778), npr-1(ad609);nlg-1(ok259), npr-1(ad609);nrx-1(wy778);nlg-1(ok259), and solitary controls. E) Representative images of aggregation behavior in npr-1(ad609);nlg-1(ok259), npr-1(ad609);nrx-1(wy778); nlg-1(ok259) and solitary controls (Scale bar = 1mm). Data for npr-1 and npr-1;nlg-1 is plotted in 3B, 3C, and 3D. Data for solitary controls is plotted in 3B and 3C.