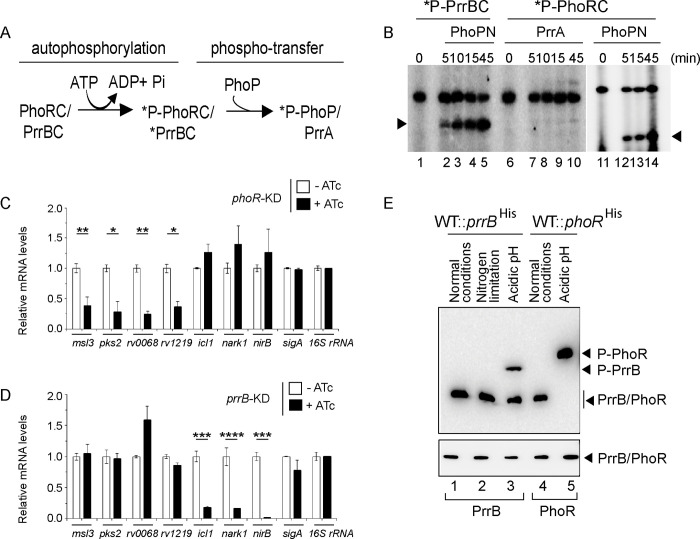
Fig 6. A non-canonical pathway of phosphorylation of PhoP.
(A) Schematic diagram of auto-phosphorylation of SKs and subsequent phospho-transfer to RRs. (B) Phosphotransfer assays from radio-labelled PrrBC to PhoPN (lanes 1–5), PhoRC to PrrA (lanes 6–10), and PhoRC to PhoPN (lanes 11–15) are detailed in the Methods. Following SDS-PAGE analyses the reaction products were digitized by a phosphorimager (GE Healthcare); lane 1 and lane 6 resolve radio-labelled PrrBC and PhoRC, respectively. (C-D) mRNA levels of a few representative pH-inducible genes were next determined in the (C) phoR and (D) prrB knock-down (phoR-KD and prrB-KD, respectively) constructs, respectively, grown under low pH conditions of growth. Each value is an average of duplicate measurements originating from biological duplicates (*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001). RT-qPCR measurements were performed as described in the Methods. (E) Phos-tag Western blot analysis of cell lysates prepared from WT-H37Rv harbouring His-tagged prrB. The bacterial strain was grown under normal conditions (pH 7.0) or indicated stress conditions, as described in the Methods, and the proteins of interest were detected by anti-His antibody. Data are representative of two independent experiments. As a loading control, His-PrrB or His-PhoR was detected from comparable amounts of cell lysates by Western blotting using anti-His antibody.