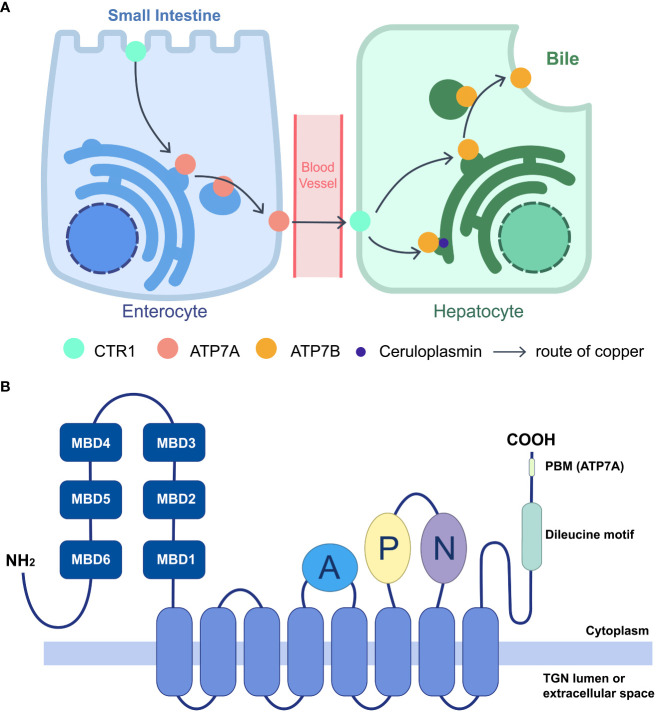
Figure 1.
Function of ATP7A/B in systematic copper distribution and their domain structure. (A) Copper homeostasis is maintained largely by importer CTR1 and exporter ATP7A/B. Cu is absorbed in small intestine by enterocytes, through the apical CTR1, and the efflux is mediated by ATP7A, transporting Cu into blood vessels. After intake by CTR1 on hepatocytes, Cu is loaded on cuproproteins, including ceruloplasmin at TGN, or secreted to bile when redundant copper accumulating, which are both mediated by ATP7B. The lack of ATP7A/B would lead to different kinds of copper deficiency. (B) Schematic diagram of the membrane topology and main domains of the P1B-type ATPase, ATP7A/B. ATP7A/B contains an eight-helices transmembrane domain (marked blue) to form a pore, connecting with three cytoplasmic domains including A (marked purple), P (marked lemon), N (marked green). The N termini lies six MBDs (marked dark blue) and C termini contains a dileucine motif (marked green). For ATP7A, a class I PBM is located on the C terminus (DTAL).