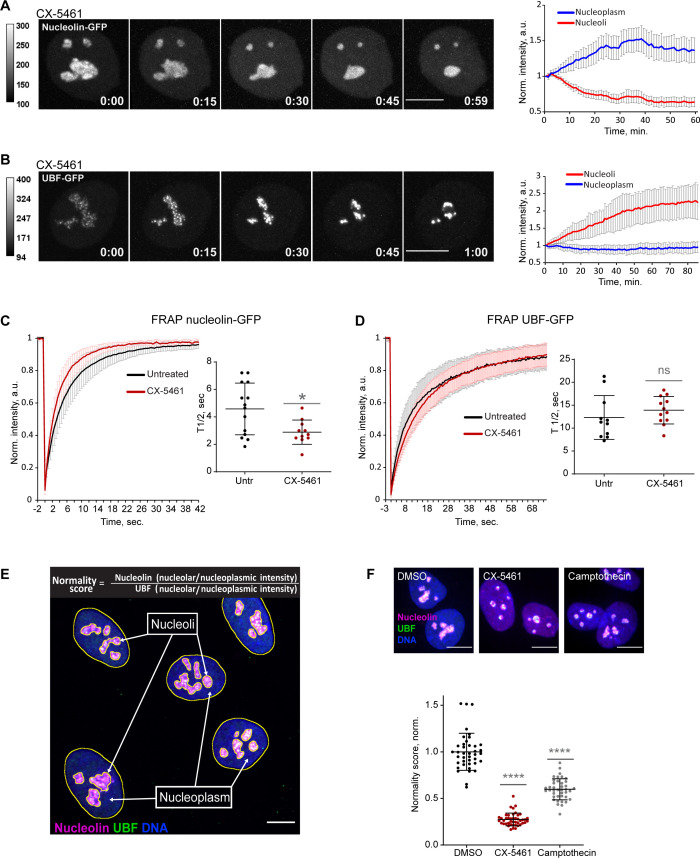
Figure 1. Nucleolar normality score as a parameter for measuring nucleolar stress.
(A) Time-lapse images of eGFP-nucleolin expressing cell treated with 2.5 µM Pol I inhibitor CX-5461 at time 0 are shown. Nucleoli shrink and round up forming small circular remnants. Fluorescence intensity, indicated by the heatscale, decreases in nucleolar remnants and increases in the nucleoplasm. The complete video sequence is shown in Video 1. Bar, 10 µm. The plot on the right shows the average intensity of eGFP-nucleolin in nucleoli and in the nucleoplasm normalized to the initial intensity at time 0. The plot is an average of 10 cells, bars denote standard deviation. (B) Time‐lapse images of eGFP‐UBF expressing cell treated with 2.5 μM CX‐5461 at time 0 are shown. UBF condenses on the periphery of nucleolar remnants forming stress caps of high fluorescence intensity. The complete video sequence is shown in Video 2. Bar, 10 μm. The plot on the right shows the average intensity of eGFP‐UBF in stress caps and in the nucleoplasm normalized to the initial intensity at time 0. The plot is an average of 13 cells, bars denote standard deviation. (C) Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) analysis of eGFP-nucleolin in untreated cells and cells treated with 2.5 µM CX-5461 is shown. The plot is an average of normalized fluorescence intensities of 14 and 10 cells. Bars denote standard deviation. The graph on the right shows corresponding individual T1/2 measurements. Asterisk indicates p<0.05 (t-test comparing the drug-treated group to untreated). (D) FRAP analysis of eGFP-UBF in untreated cells and cells treated with 2.5 µM CX-5461. The plot is an average of normalized fluorescence intensities of 11 and 12 cells. Bars denote standard deviation. The graph on the right shows corresponding individual T1/2 measurements. t-test did not detect a significant difference between the two treatments. (E) The immunofluorescence image illustrates the Nucleolar Normality score measurement. RPE1 cells were labeled with antibodies against nucleolin and UBF and counterstained with DAPI. Segmentation of nucleolar regions was performed on UBF, and whole nuclei were segmented on DAPI. Nucleoplasm regions are areas within the nuclei without nucleoli. The nucleoplasmic intensity was calculated by subtracting the integrated intensity of nucleoli from the integrated intensity of the whole nuclei. For both nucleolin and UBF, the integrated intensity of the nucleolar regions of each cell was divided by the integrated intensity of the nucleoplasm of that cell, giving the nucleolar/nucleoplasm ratio. Dividing the nucleolar/nucleoplasm ratio of the nucleolin by the nucleolar/nucleoplasm ratio of the UBF provides a nucleolar normality score for each cell. (F) Normality score measurements of individual cells treated with DMSO (vehicle), 2.5 µM CX-5461, or 5 µM topoisomerase inhibitor camptothecin, normalized to the average value of DMSO-treated cells. More than 40 individual cells were measured for each condition. Asterisks indicate p<0.0001 (unpaired t-test comparing drug-treated groups to DMSO).