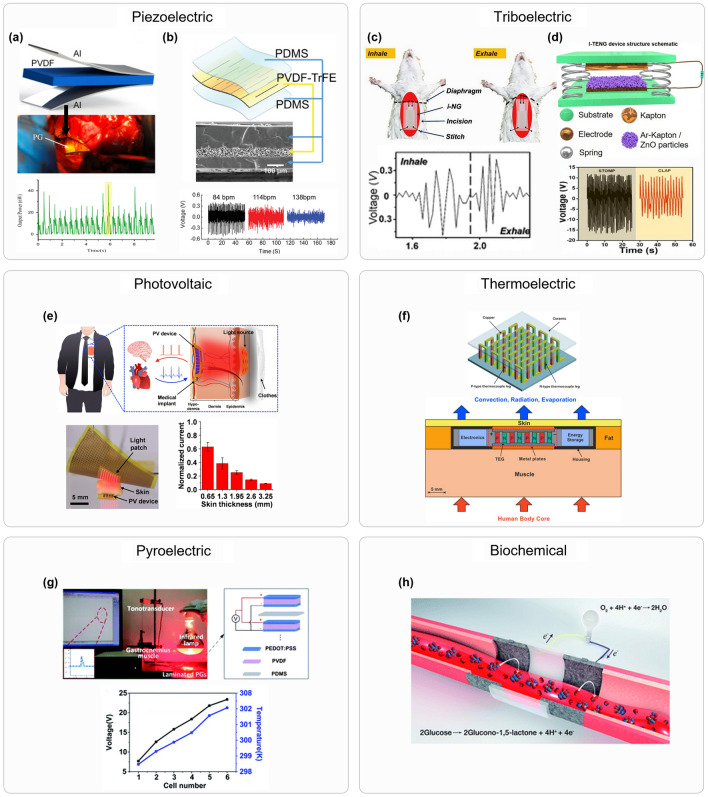
Fig. 4.
Energy harvesting techniques. Piezoelectric (a, b): a illustration of the piezoelectric generator to collect energy from the pulse in the aorta, its implantation and graph of the obtained power. Reproduced with permission [36].
Copyright 2015, Elsevier. b Diagram of piezoelectric generator based in a Kirigami design, image of the assembled device, and voltage waveforms. Reproduced with permission [38]. Copyright 2021, Wiley–VCH. Triboelectric (c, d): c diagram of the working principle of a triboelectric generator that harvests energy from breathing and a graph of the voltage collected by such device. Reproduced with permission [39]. Copyright 2018, ACS. d Schematic of the design of the ion-implanted TENG and its voltage output. Reproduced with permission [40]. Copyright 2021, Elsevier. Photovoltaic: e diagram of possible utilization of the implanted PV device coupled with a micro-LED wearable device, and a graph of the obtained current at different implantation depths. Reproduced with creative commons license [45]. Thermoelectric: f render of thermoelectric generator and diagram of the device implanted below the skin. Reproduced with permission [106]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier. Pyroelectric: g image of the device under test conditions and diagram of multicell connection with a graph showing the voltage obtained. Reproduced with creative commons license [82]. Biochemical: h diagram of implanted biofuel cell. Reproduced with Creative Commons License [83]