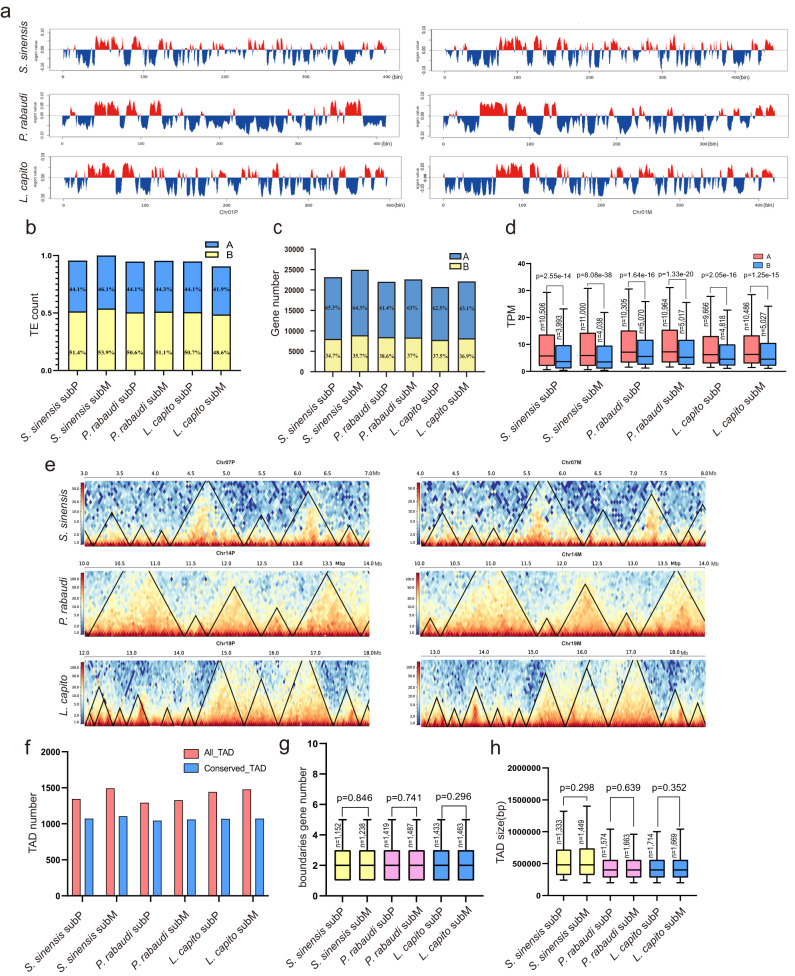
Fig. 6. Three-dimensional (3D) genome architectures, including A/B compartments and topological associated domains (TADs), of each subgenome from three allotetraploids.
a First principal component values representing A/B compartments in the Chr01P and Chr01M of S. sinensis, P. rabaudi, and L. capito. Positive PC values showing in red are designated as A compartments, and negative PC values indicating in blue represent B compartments. A/B compartments found in the rest chromosomes of three species are shown in Supplementary Figs. 45–47. b TE content in A/B compartments in subP and subM. c Gene number in A/B compartments in subP and subM. d Expression level of genes in A compartments was significantly higher than those in B compartments (Two-sample t-test; p < 0.001). e TAD structure in one representative region of homologous chromosomes from three allotetraploids. Black triangles show TADs. Yellow blocks indicate strong signal of chromatin interactions and blue blocks indicate weak signal of chromatin interactions. f Number of TAD (red) and conserved TAD (blue) identified in each subgenome. g Gene number in TAD boundaries in each subgenome. h TAD size in each subgenome. All the t statistical test used in this figure was two-sided, and the exact p values were also showed. It indicates non-significant in two-sample t-test results if p values were larger than 0.05. The sample size used for statistical analysis is shown as “n”.