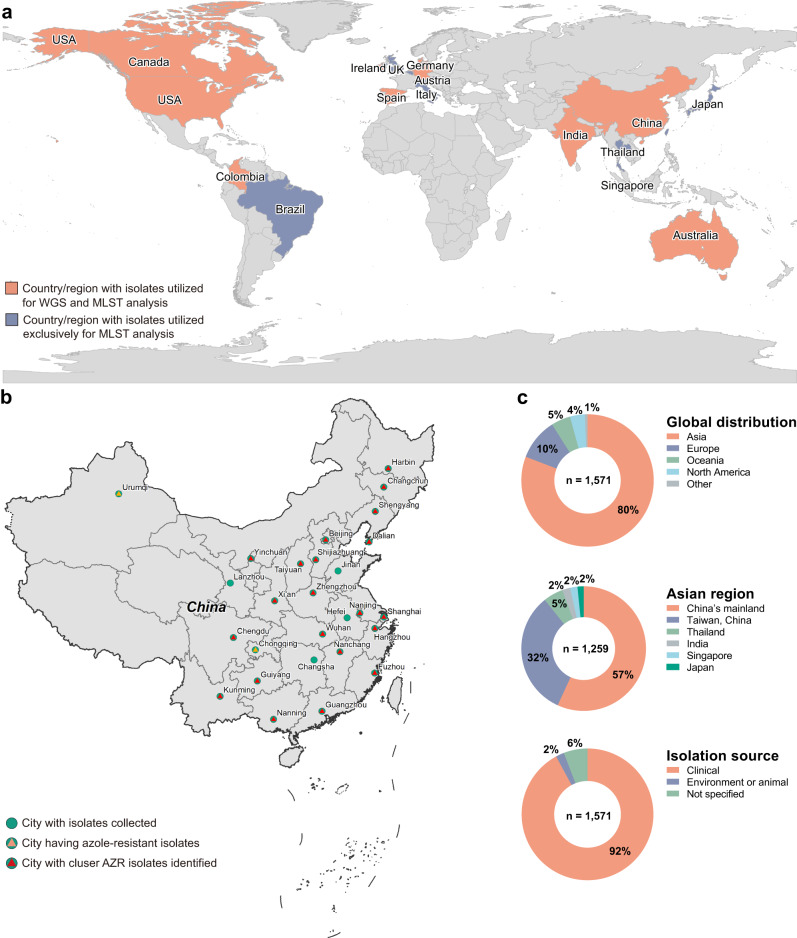
Fig. 1. Geographic distribution of C. tropicalis isolates involved in this study.
a Global geographic origins of 1571 C. tropicalis isolates used for multilocus sequence typing (MLST) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) analyses in this study by country. The collection of isolates included (A) 629 C. tropicalis isolates with WGS results, including 181 international strains that were described in nine previous studies, and 448 strains causing human invasive fungal diseases (IFDs) in China (country labeled in orange, Supplementary Data 1), and (B) 942 isolates from previous publications or an online MLST database with MLST information (country labeled in blue, Supplementary Data 2). b Geographic distribution of 448 C. tropicalis isolates collected in China by city (labeled with green circles). Cities from which azole-resistant strains and phylogenetic cluster AZR isolates were collected are labeled with orange and red triangles embedded in the green circles, respectively. c Detailed information on the proportion of C. tropicalis isolates collected, including global distribution for 1571 isolates by continents (1c top), distribution for 1259 isolates collected in Asia by region (1c middle), and strain isolation source (1c bottom).