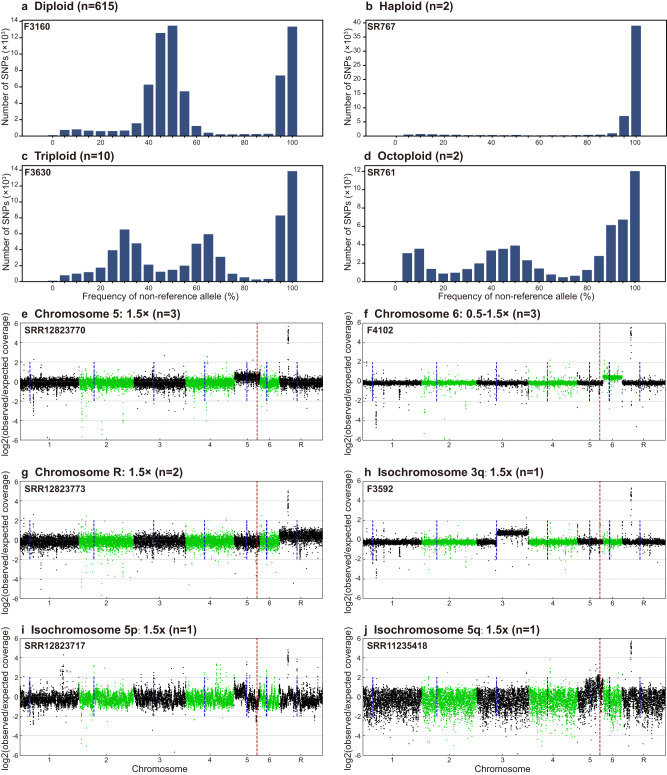
Fig. 4. Polyploidy and aneuploidy events observed in genomes of C. tropicalis isolates.
Results from representative strains are given for the different types of events, with strain ID no. labeled in the top-left corner of each figure. a–d Polyploidy analysis based on the frequency of the non-reference allele for all heterozygous biallelic SNPs across the genome. The x-axis indicates the frequency of the non-reference allele, and the y-axis represents the cumulative number of SNPs. a Diploid isolates with peaks of allele frequency observed at 0.5. b Haploid isolates with peak of allele frequency not observed before 0.95. c Triploid isolates with peak of allele frequency found in the range of 0.33 and 0.66. d Octoploid isolates with peaks of allele frequency found at 0.12, 0.5 and 0.87. e–j Aneuploidy events, which were confirmed by elevated coverage at the relevant locus (shown as dot plots: each dot represents a 1000-bp region, with green and black representing different chromosomes). The chromosome number is shown on the x-axis, and log2(observed/expected coverage) is shown on the y-axis (where expected coverage is the average genome-wide coverage for a corresponding isolate). Coverage changes are given along with the number of isolates having corresponding events in the subtitles of each figure. Blue dash lines indicate centromere positions. Red dash lines indicate the position of the ERG11 gene. e Chromosome 5 aneuploidy. f Chromosome 6 aneuploidy. g Chromosome R aneuploidy. h Isochromosome 3q. i Isochromosome 5p. j Isochromosome 5q.