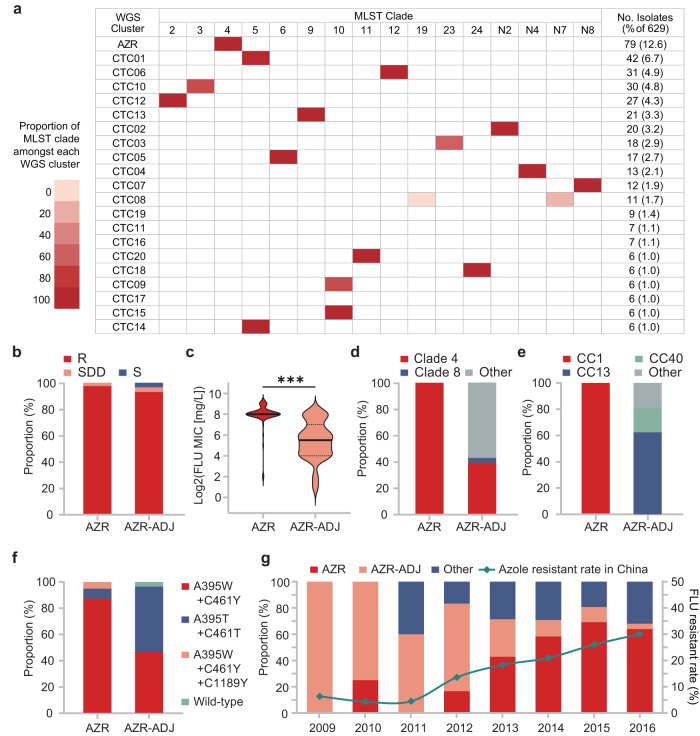
Fig. 6. Characterization of the associations of WGS phylogenetic cluster AZR and group AZR-ADJ with azole resistance and their changes over time.
a Association between MLST clades and WGS clusters. b The overall fluconazole (FLU)-resistant (R), susceptible-dose-dependent (SDD) and susceptible (S) rates of cluster AZR and group AZR-ADJ isolates. Both groups had a resistance rate of >92.8%. c A comparison of the distribution of fluconazole MICs between cluster AZR and group AZR-ADJ. The majority of cluster AZR isolates were found to be highly resistant to fluconazole (MIC ≥ 256 mg/L), which is distinct from group AZR-ADJ isolates, most of which exhibited low to moderate levels of azole resistance. ***p-values < 0.001. d, e Differences in the proportion of major MLST clades and clonal complexes (CCs) within the two populations, respectively. f Key nucleotide mutations observed in the ERG11 gene carried by cluster AZR and group AZR-ADJ isolates. g The proportion of cluster AZR and group AZR-ADJ isolates among fluconazole-resistant strains over time, and the correlations of these trends with changes in the C. tropicalis fluconazole-resistance rate in China.