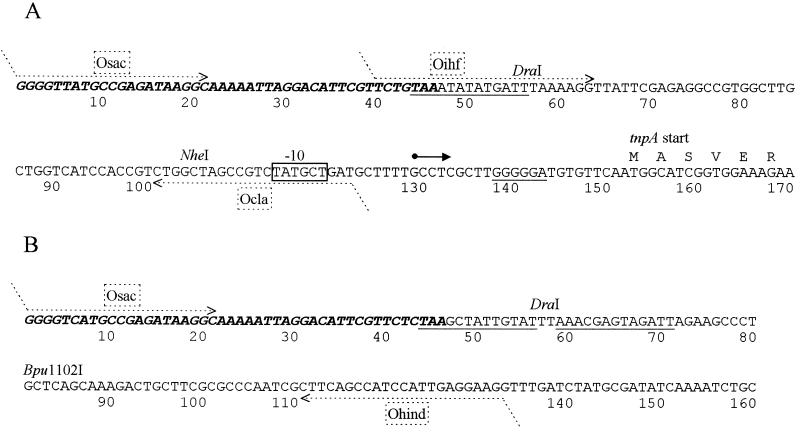
FIG. 2.
Sequence analysis of the right end (A) and left end (B) of Tn4652. The 48-bp inverted repeats are in boldface italics. Potential IHF-binding sites resembling the E. coli IHF-binding consensus sequence WATCAANNNNTTR and ribosome-binding site of the tnpA gene are underlined. The transcription start of tnpA is indicated by the solid arrow, and the putative −10 hexamer of the promoter is boxed. The deduced amino acid sequence of the tnpA gene is presented starting from the second ATG. The first six amino acids are shown. Locations of primers used in PCR for cloning of the tnpA promoter and for generating DNA fragments for the gel mobility shift assay are indicated by dotted-line arrows. 5′ ends of the oligonucleotides not complementary to the termini of Tn4652 are indicated by sloping dotted lines. Primers Osac, Oihf, and Ocla contain restriction site SacI or ClaI for cloning of the tnpA promoter.