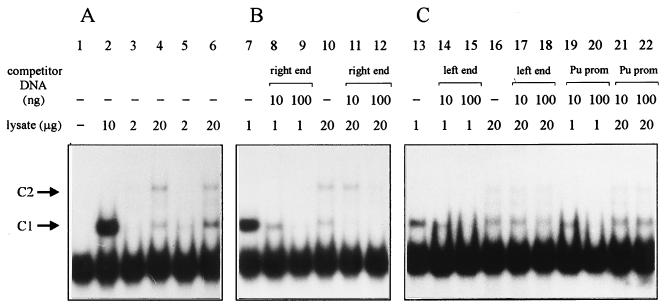
FIG. 7.
(A) Gel shift assays demonstrating specific binding of some unknown factor(s) of P. putida to the right end of Tn4652; (B) competition with nonlabeled right-end DNA; (C) competition with DNA fragments containing either the left end of Tn4652 or the Pu promoter region. The two complexes (C1 and C2) formed are indicated by arrows; C1 in lanes 2, 7, 8, 13, 14, and 19 represents binding of IHF from E. coli HB101 cell lysate to the DNA probe. Cell lysates used were from E. coli HB101 (lanes 2, 7 to 9, 13 to 15, 19, and 20), P. putida PaW85 (lanes 3, 4, 10 to 12, 16 to 18, 21, and 22), and P. putida A8759 defective in the ihfA gene (lanes 5 and 6). No cell lysate was added to the reaction mixture in lane 1. In some experiments, a weak band between C1 and C2 was detected when P. putida crude lysate was used.