Figure 2.
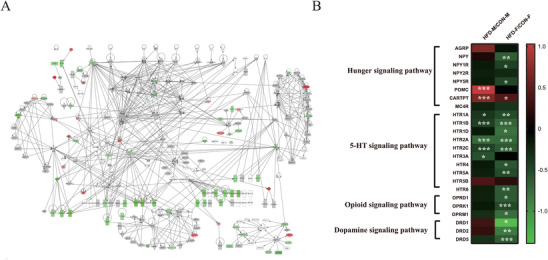
The sex‐differential effects of maternal HFD feeding during lactation on the hypothalamic transcriptome signature in early postnatal offspring mice. A) Maternal HFD feeding during lactation downregulated the key hypothalamic hunger and feeding and hedonic pathways in early postnatal offspring female mice (n = 5). Red indicates the upregulation, green indicates the downregulation, and gray indicates no significance. The intensity of the color is related to the absolute values of log10 (p‐value). B) Heatmap showing the effect of maternal HFD on the expression of genes in hunger, 5‐HT, opioid, and dopamine signaling pathways in both early postnatal male and female offspring mice. AGRP, Agouti Related Neuropeptide; NPY, Neuropeptide Y; NPY1R/2R/5R, Neuropeptide Y receptor Y1/Y2/Y5; POMC, proopiomelanocortin; CARTPT, Cocaine and amphetamine‐regulated transcript prepropeptide; MC4R, Melanocortin 4 Receptor; HTR1A/1B/1D/2A/2C/3A/4/5A/5B/6, 5‐Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 1A/1B/1D/2A/2C/3A/4/5A/5B/6; OPRD1, Opioid Receptor Delta 1; OPRK1, Opioid Receptor Kappa 1; OPRM1, Opioid Receptor Mu 1; DRD1/2/5, Dopamine Receptor D1/2/5. Values are represented as mean ± SEM and analyzed by unpaired Student's t‐test. Differences with p < 0.05 were considered significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p< 0.001.
