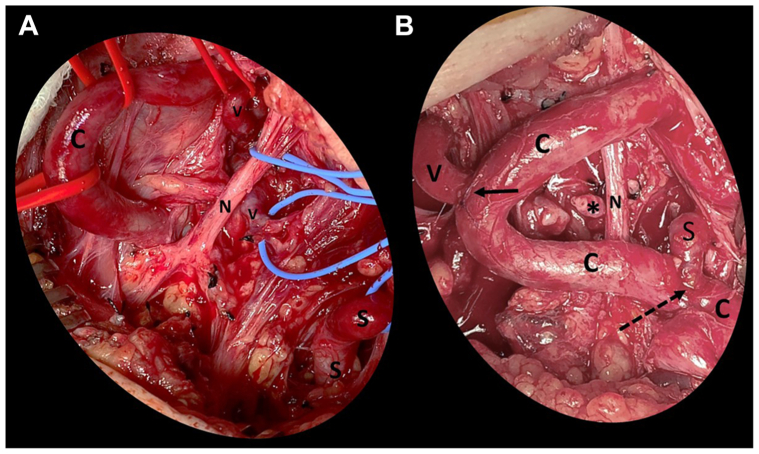
Fig 2.
Intraoperative photographs of the first stage of repair: left vertebral and left subclavian artery (SCA) transposition onto the left common carotid artery. (A) Exposure of the left common carotid (C), vertebral artery (V), and SCA (S). The vagus nerve is identified and preserved (N). The head is oriented toward the top of the photo; the torso towards the bottom. The exposed arteries demonstrate severe tortuosity. (B) Completion of the left vertebral artery transposition to the right lateral aspect of the common carotid artery (solid arrow) and the left subclavian artery transposition to the left lateral aspect of the common carotid artery (dotted arrow). The ligated proximal end of the vertebral artery is marked with an asterisk. The SCA anastomosis is 5 cm proximal to the vertebral anastomosis. Note the hairpin turns of the common carotid artery.