Figure 5: Post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms in the cytoplasm that control stem cell quiescence.
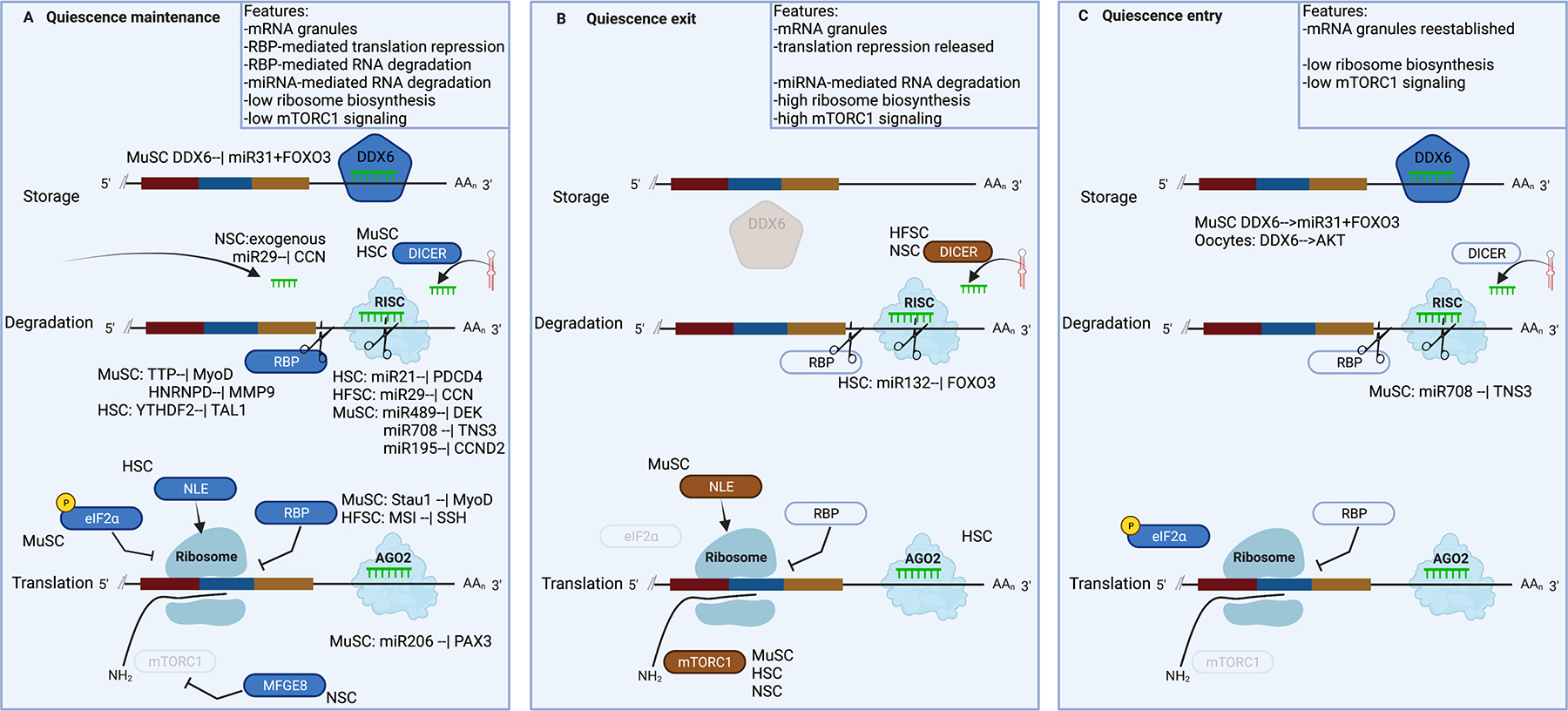
The mature mRNA can be degraded by miRNA-containing RISC complexes or RNA binding proteins (RBPs) with RNAse activity like TTP, stored in granules like DDX6-containing p-bodies, or translated by ribosomes. Translation can be regulated by RNA binding proteins like STAU1 (Staufen 1) or by mTORC signaling, and by phosphorylation of eIF2a.
DDX6, DEAD-box helicase 6; MYF5, myogenic factor 5; miR, microRNA; 3’UTR, 3’ untranslated region; DICER, double-stranded RNA-specific endoribonuclease; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex; RBP, RNA-binding protein; MyoD, myogenic differentiation 1; HNRNPD, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D; MMP9, matrix metallopeptidase 9; YTHDF2, YTH N6-methyladenosine RNA binding protein 2; TAL1, T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia protein 1; PDCD4, programmed cell death 4; DEK, DEK proto-oncogene; TNS3, tensin 3; CCND2, cyclin d2; CDC25A,B, cell division cycle 25a,b; NLE1, notchless homolog 1; eIF2a, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2A; MSI, musashi RNA binding protein 1; SSH, slingshot protein phosphatase; PAX3, paired box 3; AGO2, argonaute 2; mTOR1, mammalian target of rapamycin 1; MFGE8, milk fat globule EGF and factor V/VIII domain containing; FOXO3, forkhead box o3; AKT, AKT serine/threonine kinase, also known as protein kinase b.
